EMI/PSP LICENSE 2026
One of the leading law firms in Regulated United Europe , we excel in establishing companies with financial licenses across Europe. At EMI/PSP License, we help make things easier for our clients by streamlining processes in the most efficient and simplest manner. We appreciate the value of your time, which is why we can provide you with pre-approved solutions that licensed payment institutions expedite your journey.
Find operating companies licensed for financial activity in different European countries. For each entity, you will receive foundation date, authorized capital, number of employees, acquisition cost. Contact our team for the best solution for your financial project.
Ready-made companies with EMI/PSP license for sale
EMI/PSP LICENSE 2026
A company licensed as a payment institution in Europe
A licensed payment institution is an ideal solution for providers of financial services, Fintech companies, and startups who participate in the business of paying and transferring money. The license as a payment institution is the most popular license within such a wide array of activities as providing means of payment for online stores.
Services that can be provided to the payment institutions
- Services that enable you to put cash in a current account.
- Services enabling cash to be placed on a current account.
- Payment transactions, including transfers of funds on the request of the payment service user with respect to direct debit, including one-off direct debit, payment card or similar instrument, and credit transfer.
- Payment transactions execution where the funds are covered by a line of credit covered for the payment service user.
- Issuance and/or acquisition of payment instruments, including cooperation of one or more intermediaries in any of the aforementioned activities.
- Money orders.
- Initiation of payments (PSD2 implementation).
- Account Information (PSD2 implementation)
A company with an electronic money license in Europe

A licensed electronic money institution will enable you to offer a wider array of financial services compared to a payment institution. An electronic money institution licensed in one of the members of the European Union opens up opportunities for doing business and offering services in all other countries within the EU, using the common market restrictions and additional requirements of national regulators.
SEPA stands for Single Euro Payment Area, covering the whole of the European Union, the European Economic Area, Switzerland, Monaco, San Marino, Andorra, Gibraltar, Liechtenstein, Holy See (the Vatican), Jersey, and Isle of Man. The Single Euro Payment Area is an area where 500 million consumers and over 20 million companies pay and receive payments in euros with low or nil charges, under the same general conditions, rights, and obligations, irrespective of their location in Europe. The licensed electronic money institutions may join SEPA directly, just like banks, and open individual IBAN accounts for their clients. With the EMI license, a company can create sub-accounts for its customers within its bank account and thus has the chance to develop electronic wallets. Accordingly, the clients can change cash for the electronic version of coins and banknotes issued by the firm and store in their e-wallet.
Services that can be offered to an electronic money license holder company:
- Deposit and payout of customer funds
- Payment transactions, excluding payment transactions with the use of credit
- Acquiring
- Money transfer
- Payment initiation services
The difference between a payment institution (PSP) and an electronic money institution (EMI)
Only EMI differs from the two types of payment service providers in respect of issuance of electronic money or digital currency, such as a cash balance recorded on an electronically stored value card-also called a prepaid card-on an account-electronic wallet-or another device.
Why you should choose a ready-made solution
Our company is constantly striving to find the most convenient solution for customers, since in fact, the time of preparation of documents and receiving a financial license in Europe takes from 9 to 18 months. Below you can find ready-made proposals for already existing payment institutions and companies with a valid EMI license. If you want to start your financial business in Europe as soon as possible, our legal team will be happy to offer you a few options depending on your preferences and needs. In 4 weeks, you will be ready to start your activity as a payment institution or an EMI operator. Our experts will be happy to help you with the choice of the most appropriate option that will meet your project. Top EMIs in Europe.
Top EMIs in Europe


How to get an EMI/PSP License in Europe
In today’s financial services industry, the role of digital payments and financial technologies or fintech is becoming increasingly important in view of the high demand for security, efficiency, and novelty in the sphere of payment solutions. Thus, in the digital payments market alone, the number of users is expected to reach over 601 mill. users by 2027.
Licensing to operate in this prospective sector comes in the form of an Electronic Money Institution and Payment Service Provider license. EMI and PSP licenses are the modern key to shaping the future of electronic payments, since businesses with those can legally provide everything from e-money issuance to payment processing.
In Europe, these licenses are the subject of intricate regulatory regimes and requirements, which is why it is so important for a financial institution to analyze relevant regulations before selecting the most appropriate European jurisdiction for an EMI/PSP license. A license from a reputable jurisdiction can affect how customers and partners view your business, and how far they trust it enough to make use of your financial services on offer.
What is an Electronic Money Institution License?
The EMI license is a form of regulatory authorization through which financial institutions or companies desiring to provide electronic money issuance and payment services receive from the central bank of the country where the license is issued. EMIs form an important feature in the financial ecosystem since they are, more often than not, at the leading edge of FinTech innovation, forcing improvements in digital methods of paying for goods and services, mobile banking applications, and online financial services, hence changing the face of the financial industry.
The activities that an EMI license holder is allowed to carry out include the following:
- To issue an electronic money, which is a digital representative of funds stored in a digital form and considered to be a means for carrying out various financial operations, including online purchases, money transfers, and bill payments;
- To perform payment services for individuals, businesses, and organizations by processing card payments, facilitating bank transfers, and maintaining online payment platforms;
- Provide digital wallet services wherein electronic money is stored securely on a digital platform, thereby enabling users to make payments, transfer funds, and manage their finances digitally.
What Is a Payment Institution (PI), or Payment Service Provider (PSP), License?
In general, the license of a payment institution or provider is the regulatory permission for a selected jurisdiction from the financial authority with the purpose of enabling its holder to conduct a wide range of payment services for both consumers and businesses as well as various forms of organizations. Generally speaking, licenses are one of the underlying components of the financial regulatory system and very essential for companies that facilitate electronic payment methods and financial transactions.
Here’s what a holder of a PI/PSP license can do:
- Process debit and credit card payments for merchants and consumers
- Provide domestic and cross-border money transfers and remittances
- Set up and manage direct debit transactions, like bill payments
- Electronically initiate payment on behalf of customers
- Provide customers with a consolidated view of their financial accounts
Benefits of EMI or PI/PSP License in Europe
Here are a few of the advantages of an EMI or PI/PSP license that can be obtained within Europe for financial institutions and companies:
- Access to the large EU market comprising 27 member countries, thereby enabling the license holders to provide payment services and products of electronic money to a very large customer base.
- Undoubtedly, the license obtained from a renowned European regulator enhances the credibility of the company, and building trust in customers, partners, and investors follows thereupon.
- These include passporting rights, which make the process of expansion much easier and less burdensome, given that EMI and PI/PSP license holders are entitled to provide their services and exercise their activities in several EU countries without any additional licenses from the competent authorities of the state they are operating in.
- The EU is the global fintech innovation hub, and a European EMI or PI/PSP license places the licensees right at the center of a rapidly changing world of payments and fintech.
- A European EMI or PI/PSP license enables cross-border transactions within the EU and customers with the ability to send and receive money across various European countries with ease.
- Regulatory guidance and support by the authorities with many years of experience help companies holding a European EMI or PI/PSP license satisfy even the most complicated compliance requirements.
- Holding a European EMI or PI/PSP license provides legal protection, thus guaranteeing that the firm is compliant with prevailing laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues and penalties.
- EMI or PI/PSP license holders from Europe are allowed to expand into the non-EU market on the basis of their regulatory experience, taking with them a reputation for good credibility and expertise.
EMI and PI/PSP Regulations in Europe
Under the conduct requirements, European EMIs and PIs/PSPs must adhere to strict but innovation-friendly norms that provide for stability and security in the financial system for consumers against various aspects, prohibition of financial crimes, promotion of competition, and innovative solutions in the payment industry.
For EU/EEA-based EMIs, e-money rules under the Electronic Money Directive, EMD 2009/110/EC, specifically provide for:
- Definition of electronic money
- Issuance of electronic money within the regulatory requirements
- Initial and ongoing capital requirements
- Requirements to safeguard customer funds and to protect them against insolvency
- Standards on operations and security; AML/CFT requirements
- Rules on passporting rights for operations across the EU/EEA countries
EU/EEA-based PIs/PSPs are regulated under the Payment Services Directive (PSD 2007/64/EC and PSD2 2015/2366) that includes, among others, the following:
- The definitions of payment services, including payment initiation, account information, and execution of payment transactions
- Regulatory requirements for PIs/PSPs: capital adequacy, governance, customer protection
- Under PSD2, all licensees are under obligation to adopt SCA and secure communication in order to increase online payments security
- Access to Accounts: XS2A provisions allow third-party providers access to customer account information with consent
- Passporting rights regulations allow PIs/PSPs to operate freely across various EU/EEA countries with a single license obtained from one EU/EEA country.
Both EMIs and PIs/PSPs are subject to the following EU legislation:
- EU Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD) that require such institutions to put in place effective AML/CFT mechanisms to forestall money laundering and financing illegal activities
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) lays down the principles for data protection of individuals, consent requirements, and obligations related to reporting data breaches
- Interchange Fees for Card-Based Payment Transactions Regulation (EU) 2015/751: establishes interchange fee caps with regard to card-based payment transactions
- Regulation on Cross-Border Payments (EC) 924/2009: As this Regulation will imply transparency and fairness in cross-border payment services, the regulation will be relevant to cross-border money transfer services
- Multilateral Interchange Fees for Card-Based Payment Transactions Regulation (EU) 2015/751: interchange fees with regard to card-based payment transactions
- (EC) 260/2012: This regulation on cross-border payments in the EU is targeted at reducing the costs of cross-border payments and at making the charges for currency conversion more transparent.
- (EU) 2018/389: The regulation on interchange fees for card-based payment transactions changes and expands the one regulating interchange fees for card-based payment transactions.
It is worth noting that, although many of the above-mentioned laws are transposed into the national legislation of every EU country, each national regulatory framework has to be dealt with separately, as they differ notwithstanding consolidated laws. For a complete identification of licensing procedures and requirements of continuing compliance in a certain European jurisdiction, please contact our team of experienced lawyers here at Regulated United Europe, and we will make an appointment for your personal consultation.
Top 8 countries granting the highest number of PI, EMI and AISP authorization in EU
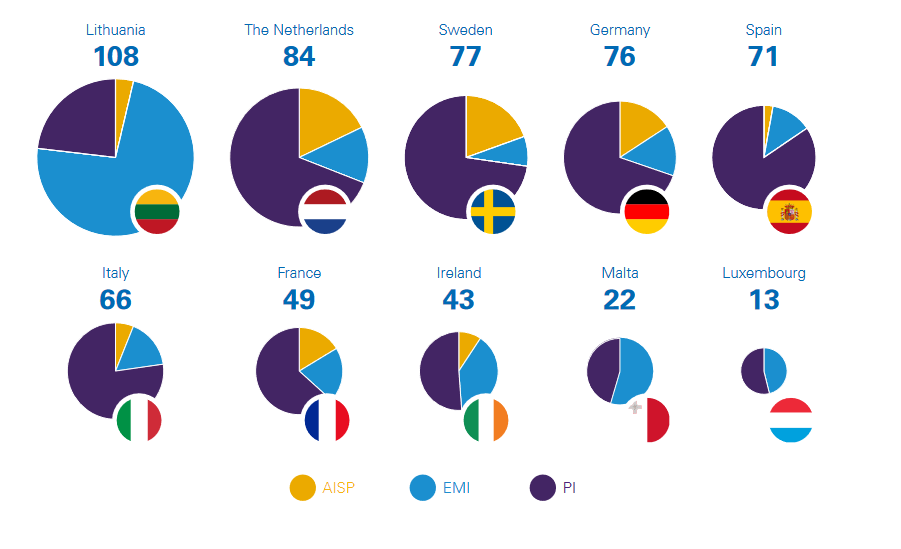
Top European Jurisdictions for an EMI or PI/PSP License
The decision on the place of incorporation for an EMI or PI/PSP in Europe is very important because each European country has different advantages, regulatory environments, and market opportunities. You may want to choose a jurisdiction based on your business model, resources, target market, and timeline.
In the last years, Lithuania has emerged as an EU member country with a very popular jurisdiction to obtain either an EMI or PI/PSP license. It’s well-known for its efficient and agile licensing process in reference to EMIs and PIs/PSPs since the regulatory authority, the Bank of Lithuania, usually issues one of these licenses in 3 months. It has actively pursued the adoption of innovation in the financial sector, and it is an ideal place for companies seeking to build ground-breaking financial services solutions.
Finally, not least, Lithuania joined the Single Euro Payments Area with the purpose of encouraging cross-border euro-denominated transactions within the involved European countries, while licensing opens access to a huge European market for payment services.
Another very friendly jurisdiction within the EU and SEPA is Estonia, which is one of the most popular countries in which to get an EMI or PI/PSP license. The application process may take as long as 6 months, which is rather efficient compared with the rest of Europe. The Financial Supervision Authority regulates the licensees and gives ample guidelines on how to present quality applications that will lead to positive results. With its highly developed digital infrastructure and multiple e-government initiatives, Estonia has become the right environment for fintech companies. Besides, it offers a competitive Corporate Tax rate of 20%, thus allowing cost-effective operation for licensed companies.
Malta is one of the most well-known and reputable jurisdictions within the EU to obtain an EMI or PI/PSP license. The Malta Financial Services Authority is in charge of supervising the Maltese financial services and shows a very strict following of EU regulations in its desire to keep the climate stable to allow licensees to win confidence with clients, partners, and investors. Despite these strict regulations, MFSA can usually succeed in providing one of these licenses within 3-6 months. Also, Malta does offer some tax benefits, such as low effective Corporate Tax rate and no withholding tax on dividends paid to non-resident shareholders, for firms operating in financial services, making it financially attractive for businesses.
The UK is also one of the favorable jurisdictions to obtain both EMI and PI/PSP licenses due to its well-developed and dynamic financial ecosystem. It has a high-profiled fintech industry and gives great conditions to companies willing to develop some sort of innovative payment solutions. The Financial Conduct Authority-abbreviated FCA, is the UK’s regulatory authority responsible for conduct supervision of financial services. It enjoys a high reputation due to its powerful regulative framework and protection of consumer rights which makes licensees trusted and reliable businesses in the eyes of clients, partners, and investors. One of these licenses can be issued, depending on completeness of the submitted application, in anything from 3 to 12 months.
Requirements for EMI and PI/PSP License Applicants in Europe
Since each European state is obliged to act under different regulatory frameworks, specific juridical requirements for EMI or PI/PSP license candidates differ from one jurisdiction to another, regardless of the overall EU-wide laws. You can still learn more about the most common eligibility criteria and requirements that may give you a general picture in Europe.
To apply for either an EMI license or a PI/PSP license, one has to incorporate a company in the country where he/she decides to apply for a license. Private Limited Company and Public Limited Company are some of the most common legal forms a business can take on. It may take anything from a few days to several weeks depending on how the processes are done in the jurisdiction where you are incorporating, how complex the business is, and the quality of your application.
Once you have set up a company, it will be required to do the following:
- Has the minimum initial capital which usually differs from state to state but may be estimated to lie in the range from 125,000 EUR up to 350,000 EUR for EMIs and from 20,000 EUR up to 125,000 EUR for PIs/PSPs.
- Company directors and shareholders must be fit and proper as defined by the regulator in the chosen jurisdiction in terms of financial and professional integrity.
- Shall implement AML/CFT procedures and policies that are appropriate.
- Be fully compliant with the PSD2 regulation of the EU in its establishment of secure and standardized interfaces, besides ensuring secured communications with the customers.
- Shall be in possession of an appropriate technical infrastructure for offering secure financial services, which shall include the safeguarding of the funds of the customers.
- Should have a clear risk management framework that identifies all potential risks and has ways of mitigating them; these include operational risks, financial, and compliance risks.
- Application fees also vary from country to country, from several thousand euros to tens of thousands of euros.
Usually, a candidate applying for a European EMI or PI/PSP license would need to prepare the following documentation:
- A comprehensive business plan describing the envisaged EMI or PI/PSP activities—one that includes things like the type of services to be carried out, markets of operation, risks, and financial projections.
- Statutes
- A Memorandum of Association
- Details concerning each shareholder: personal information, previous financial activities, and the ownership interest of each shareholder within the company
- Description of the organizational structure of the firm
- Financial statements: balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow projections for at least a couple of years
- Confirmation of the availability of the initial capital
- Detailed description of AML/CFT procedures
- Information on the applicant’s cybersecurity measures, including encryption, protection of data, fraud prevention measures
- Technical specifications, including a description of the Company’s IT infrastructure and systems.
- Detailed description of the risk management framework.
- Evidence of insurance coverage.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery Plan.
- Procedures for formulating and filing regulatory reports to the regulator of the licensed jurisdiction.
- Customer agreements and terms of service.
Application process for EMI or PI/PSP license in one of the European countries
Though the very process of application may vary from one jurisdiction to another, there are indeed important steps you will have to consider when applying for either an EMI or a PI/PSP license in Europe. First and foremost, remember to complete your application package, as an incomplete application is likely to cause delays in processing or even be rejected. Our team will be able to support you through the process by ensuring that all the required steps are performed in accordance with the exact requirements of the authority from your chosen jurisdiction.
Application Process for a European EMI or PI/PSP License:
- Collection and compilation of all required documents and information needed for the license application.
- Paying the stipulated application fees to the regulatory authority of the chosen jurisdiction.
- The steps to be followed include: Executing the application form provided by the regulatory authority and filing the same along with the required documents to the concerned authority.
- Interviewing or attending meetings with personnel from the regulatory authority.
For such a license, during the application process, a European licensing authority would expect an applicant to give sufficient assurance that he or she will develop a proper financial undertaking that will enhance the good repute of the jurisdiction of choice, serve the interests of the public as well as look after the interests of the clients. As a rule, each applicant who is found successful is granted a license that normally has a specific term, and it is generally renewable on condition that the business concerned is seen to comply with the applicable regulations constantly and consistently.
Ongoing EMI and PI/PSP Licence Requirements in Europe
When your company is licensed to operate either as an EMI or a PI/PSP in Europe, it is supposed to meet a continuous set of demands and obligations that will keep your organization within the regulatory threshold of the jurisdictions where it operates. These ongoing demands are about ensuring customer funds safety, protecting your company against financial crimes, and keeping the integrity of the national and European financial system.
Observance of these obligations requires internal controls, regular audits, and internal or external audit procedures. Licensees are obligated to demonstrate ongoing compliance through periodic reporting to the regulatory authority with respect to accounting statements, transaction reports, and other necessary information.
Of particular significance is the obligation for compliance with the AMLD provisions binding on European licensees to:
- Constantly monitor the customer’s transactions in order to report suspicious activities without delay to the concerned FIU.
- Conduct adequate customer due diligence for all customers at the beginning of the business relationship or in cases of occasional transactions, by identifying their customers and the beneficial owners of the businesses.
- Implement enhanced due diligence measures under circumstances that present a heightened risk of money laundering or financing of terrorism.
- Record keeping: keep records of customers’ transactions, customer identification and due diligence measures for at least five years from the effective date of the termination of the business relationship.
- Identify the PEPs and their family members and close associates and take enhanced due diligence measures.
- Application of AML/CFT measures to third-party relationships: The EMI or PI/PSP extends AML/CFT measures to agents or business partners if they offer services on its behalf.
- Regular training and awareness programs should be conducted for the employees to make them aware of their role in AML/CFT compliance and to identify suspicious activities.
If you wish to obtain an EMI or PI/PSP license in Europe, our team here at Regulated United Europe will be delighted to support you in incorporating a company and applying for a license in a European jurisdiction that suits your business goals. With dedicated legal advisors, tax experts, and financial accountants at your side, you will find the processes of obtaining an EMI or PI/PSP license and registering a company in Europe easy, frictionless, and transparent. Contact us now to schedule a personalized consultation and set the stage for long-lasting success.
Also, lawyers from Regulated United Europe provide legal services for obtaining a crypto license.

“Pre-made solutions can greatly speed up acquiring an EMI/PSP license, saving substantial time compared to the lengthy licensing process. Reach out today, and I’ll lead you through the process of commencing this business.”
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is an EMI/PSP license, and why is it important for businesses in the financial sector?
An EMI/PSP (Electronic Money Institution/Payment Service Provider) license is a regulatory authorization that allows financial institutions and companies to provide various electronic payment and financial services.
It's crucial for businesses in the financial sector as it enables them to offer services like electronic money issuance, payment processing, and money transfers in full compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
What services can be provided by companies with an EMI license?
Companies with an EMI (Electronic Money Institution) license can offer services such as issuing electronic money, providing payment services, offering digital wallet services, and facilitating various financial transactions, including online purchases and bill payments.
What services can be offered by companies with a PSP license?
Companies with a PSP (Payment Service Provider) license can process debit and credit card payments, facilitate money transfers, manage direct debit transactions, initiate electronic payments, and provide consolidated views of financial accounts.
What's the difference between an Electronic Money Institution (EMI) and a Payment Service Provider (PSP)?
The main difference is that EMIs can issue electronic money (e-money), such as prepaid cards or digital account balances, while PIs/PSPs primarily focus on payment processing and transaction facilitation. EMIs have a broader range of financial services.
Why should businesses consider choosing a ready-made solution for obtaining an EMI/PSP license in Europe?
Ready-made solutions can significantly expedite the process of obtaining an EMI/PSP license and ultimately save significant amounts of time compared to the lengthy licensing process, which can take up to 18 months.
These solutions provide established companies with existing licenses, making it quicker for businesses to start their financial operations.
What are the advantages of holding an EMI or PSP license in Europe?
Some of the key advantages include:
- Access to the vast EU market
- Enhanced credibility
- Passporting rights for operating across EU countries
- Participation in fintech innovation
- Ease of cross-border transactions
- Regulatory guidance
- Legal protection
- Opportunities to expand into non-EU markets
How long does it typically take to obtain an EMI or PI/PSP license in Europe?
The time frame varies by jurisdiction and complexity. Generally, it can range from 3 months to 18 months.
However, some jurisdictions (Lithuania, for example) offer faster processing times.
What are the key requirements for EMI or PSP license applicants in Europe?
Some of the main requirements include:
- Initial capital
- Matching the fit and proper criteria for directors and shareholders
- AML/CFT procedures
- Compliance with EU regulations
- Technical infrastructure and risk management processes
- Application fees
- Comprehensive documentation
Can a licensed EMI or PI/PSP operate across multiple European countries with a single license?
Yes. Within the EU, EMI and PI/PSP license holders can leverage passporting rights to operate in multiple EU countries with a single license from an EU country.
Which European jurisdictions are popular for obtaining EMI and PI/PSP licenses, and what are their advantages?
Popular jurisdictions include Lithuania, Estonia, Malta, and the UK. They offer advantages such as efficient licensing processes, regulatory compliance, access to the EU market, and financial benefits.
What regulations govern EMIs and PIs/PSPs in Europe?
European EMIs and PIs/PSPs are subject to various regulations, including the Electronic Money Directive (EMD 2009/110/EC) for EMIs and the Payment Services Directive (PSD 2007/64/EC and PSD2 2015/2366) for PIs/PSPs.
Additionally, they must adhere to EU Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and other related regulations.
What ongoing requirements and responsibilities do EMI and PI/PSP licensees have in Europe?
Licensees must maintain internal controls, conduct regular audits, and ensure ongoing compliance with AML/CFT regulations.
They need to continuously monitor customer transactions, conduct due diligence on customers, apply enhanced due diligence in high-risk situations, and provide ongoing training for employees to ensure AML/CFT compliance.
What is the role of the chosen jurisdiction in the EMI or PI/PSP licensing process?
The chosen jurisdiction's regulatory authority oversees the application process, reviews applications, and grants licenses. Different jurisdictions may have varying processing times and requirements.
Can EMI and PI/PSP license holders in Europe expand into non-EU markets?
Yes. European license holders can leverage their regulatory experience and credibility to expand into non-EU markets. Holding an EMI or PI/PSP license may enhance trust and open opportunities in other regions.
How can a business determine the most suitable European jurisdiction for obtaining an EMI or PI/PSP license?
The choice of jurisdiction depends on factors like business model, target market, available resources, and timeline.
On top of that, it’s advisable to also consider factors like efficient processing, regulatory environment, and market opportunities when making the decision.
RUE customer support team
RUE (Regulated United Europe) customer support team complies with high standards and requirements of the clients. Customer support is the most complex field of coverage within any business industry and operations, that is why depending on how the customer support completes their job, depends not only on the result of the back office, but of the whole project itself. Considering the feedback received from the high number of clients of RUE from all across the world, we constantly work on and improve the provided feedback and the customer support service on a daily basis.
CONTACT US
At the moment, the main services of our company are legal and compliance solutions for FinTech projects. Our offices are located in Vilnius, Prague, and Warsaw. The legal team can assist with legal analysis, project structuring, and legal regulation.
Registration number:
14153440
Anno: 16.11.2016
Phone: +372 56 966 260
Email: [email protected]
Address: Laeva 2, Tallinn, 10111, Estonia
Registration number: 304377400
Anno: 30.08.2016
Phone: +370 6949 5456
Email: [email protected]
Address: Lvovo g. 25 – 702, 7th floor, Vilnius, 09320, Lithuania
Registration number:
08620563
Anno: 21.10.2019
Phone: +420 775 524 175
Email: [email protected]
Address: Na Perštýně 342/1, Staré Město, 110 00, Prague
Registration number: 38421992700000
Anno: 28.08.2019
Email: [email protected]
Address: Twarda 18, 15th floor, Warsaw, 00-824, Poland
Please leave your request
The RUE team understands the importance of continuous assessment and professional advice from experienced legal experts, as the success and final outcome of your project and business largely depend on informed legal strategy and timely decisions. Please complete the contact form on our website, and we guarantee that a qualified specialist will provide you with professional feedback and initial guidance within 24 hours.