| Step | Description |
| 1. Defining the Purpose and Vision | First of all, define the purpose and vividly envision the cryptocurrency. Answer questions like what your currency is to be used for, what problem does it solve, and what unique features or benefits it will offer. This helps establish the project’s direction. |
| 2. Choosing the Right Technology | Select a blockchain platform for your cryptocurrency. Consider various technologies like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana, and others. Each has pros and cons, and the choice should be based on technical requirements such as transaction speed, scalability, and security. |
| 3. Cryptocurrency Development | Once a platform is chosen, begin actual development, including smart contracts and defining parameters like the total number of coins and the rate of issuance. Emphasize security and code auditing. |
| 4. Mining or Premining | Decide if your cryptocurrency will be mineable (coins mined through computational operations) or pre-mined (certain coins released in advance). |
| 5. Testing | Thoroughly test your cryptocurrency and blockchain for bugs and security vulnerabilities before launch. This includes internal testing and possibly beta testing with the community. |
| 6. Legalisation and Compliance | Ensure compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements. Seek advice from legal experts regarding cryptocurrency taxation, Know Your Customer, and Anti-Money Laundering regulations. |
| 7. Launch and Promotion | After completing development, testing, and legal preparations, launch your cryptocurrency. Create a marketing roadmap detailing how social networks, blogs, forums, and media will participate. Consider an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) or Initial Exchange Offering (IEO) to attract investment interest. |
Launching the Token on Blockchain
Over the past few years, launching tokens on the blockchain has gained increasing popularity as a means to tap into funding, create a community for a project, or provide an offering within the digital asset market. These tokens can be utilized for many purposes, such as utility functions in some sort of ecosystem, representation of equity in a company, or even be tradable. Starting a token on a blockchain means a lot more than just an idea to create a token. In this article, we delve into launching a token on a blockchain—from conceptualization to implementation and promotion.
Identify Your Purpose and Vision for the Token
Clearly, defining the purpose and vision is the first step towards successfully launching a token. An important step is to determine what problem it solves, how it adds value to a user, and what function the token will perform. It will also be important to make a determination of whether the token will be classified as a utility (used within the project’s ecosystem) or a security. This classification may also have legal implications based on the country in question.
Choose a Blockchain Platform
The selection of the appropriate blockchain platform has to be performed. Popular tokenization platforms include but are not limited to Ethereum, specifically ERC-20 and ERC-721; Binance Smart Chain, BEP-20; Solana; and Polkadot. Each such platform has its own set of features, pros, and cons. The differences within those platforms relate but are not limited to transaction speed, gas costs, and level of community involvement.
Smart Contract Development
When creating a token, the developer builds a smart contract to control its application. There are the inclusion of rules and conditions within a smart contract regarding the issuance of tokens, their transferring, and management. The source code of a smart contract should be closely looked at so that vulnerabilities and bugs can be avoided.
Preliminary Testing
Prior to the main event of launching a token, it is necessary to pre-test its functionality on the test network of a chosen blockchain platform. This will be helpful for identifying issues with a smart contract and ensuring that it works correctly.
Token Launch and Smart Contract Deployment
After proper tests and finalizing the smart contract, it is deployed on the main blockchain network and the token launched. At this stage, the token is already available to the general public.
Listing on Exchanges
Listing the token on cryptocurrency exchanges will be vital. It is to ensure that the token is available for a wide range of users. This may also involve negotiations with exchanges, meeting requirements exchanges have for listing.
Community Promotion and Development
That would be things like effective marketing strategy and the development of a loyal community around the token. Social networks, forums, blogs, and collaborations with influencers can increase the visibility of the project many times over and attract interested users.
What is Cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a kind of digital or virtual currency that applies a type of cryptography for security, making it virtually impossible to counterfeit. Because of the usage of this very technology, cryptocurrencies work as decentralized systems with blockchain technology at their core—a distributed database managed by various participants of this network. Indeed, this pioneering property has so far revolutionized not only the financial industry but also offered new economic interaction and investment forms.
Principles of Cryptocurrency Operation
The most important part of any cryptocurrency is the so-called blockchain-skewed public log of all previously made transactions. Every block in a blockchain contains a set of transactions, with every new transaction message added to the log of every participant of this network. At the same time, the blockchain is both secure and open because one cannot change the data that has entered the blockchain without changing all subsequent blocks and obtaining the consent of the network.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Cryptocurrencies
| Benefits | Disadvantages |
|
|
What is the difference between coins and tokens?
In the field of cryptocurrency, constant mentions are made about “coins” and “tokens.” These are two terms that sound extremely similar, but in truth, refer to totally different things. This is a basic issue in the difference between coins and tokens that investors, developers, and users of cryptocurrency technologies really must know.
Coins versus Tokens
| Coins | Tokens |
Digital currencies that operate on their own blockchains, used as a medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value. Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum (ETH), Ripple (XRP).
|
Built on existing blockchain platforms, tokens can represent values, assets, or concepts, with a broader range of functions than coins. Types include utility tokens, security tokens, and NFTs.
|
Key Differences
The difference between coins and tokens represents a big difference in possibilities and uses of the cryptocurrency area. If coins are bases for ecosystems of cryptocurrencies and designed to represent the very function of financial transaction and trade, tokens can extend, through already implemented blockchains, various values, rights, and functions. It is in understanding of this difference that allows a better understanding of the real possibilities and prospects offered through blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
- Blockchain: Coins are independent on their blockchains, while tokens are built on currently existing blockchain platforms.
- Functionality: The principal uses of coins are for mediums of exchange and store of value. Tokens can have multiple functions: to represent assets, access services, or even vote.
- Uses: Coins are mainly used as digital currency, while tokens have many more uses – providing rights to assets or shares in a project or used in highly specialized applications and services.
Creation of a digital coin is no small undertaking and takes tremendous experience in cryptography, programming, and economics. Unlike tokens that can be developed on already existing blockchain networks like Ethereum with minimal hassle, making your own coin would mean you have to build a blockchain from scratch or fork an existing one. In this article, we will take a look at some of the key points to keep in mind if you are to create your cryptocurrency:
Defining Purpose and Vision
First of all, before creating a digital coin as such, one should consider what exactly he or she wants to achieve. It may be to create an internal use coin for a certain project, to make some transaction privacy-centric coin, or even a new currency that can be used at the global level as another means of exchange. Your decision with respect to your vision will determine many subsequent decisions.
Choosing an Appropriate Technology
This is where you actually need to decide upon a technology base for your digital coin. You can develop your own blockchain from scratch, involving much work and resources, or you can take the base of some already-coded blockchain and make modifications according to your requirement. Many altcoins are forks of Bitcoin or Litecoin because their source codes are open under free and open-source software licenses.
Development and Testing
When the technology has been chosen, the development of blockchain and cryptocurrency should start. It includes the development of programming consensus rules, the mining mechanism if any, coin parameters – maximum amount, issuance rate, etc., wallet and other tools creation for work with the currency. Testing at this stage is crucial to be performed for the security and reliability of the system.
Ensuring Security
Security is considered one of the most relevant features in any cryptocurrency. It is highly important that the code in the blockchain should be audited, ensuring no attacks and vulnerabilities are present. For that, a third-party expert or auditor specialized in cybersecurity can be used.
Launching the Network and Mining
Now that development and testing are over, it is time to go live on the network. This includes deploying the blockchain on servers, starting mining if your coin provides the mechanism, and distributing a few initial coins to early adopters and supporting users.
Promotion and Community Building
This means the popularization of your cryptocurrency and the creation of an active community around it. It also implies PR and marketing campaigns, conferences of cryptocurrencies, publications in social networks, and forums. One more point to contribute to popularity and value growth is the development of an ecosystem of applications and services using your coin. The popularity of this coin is determined by whether there are any applications and services developed on its basis.
Creating Your Own Token
Creating your own token is a promising and exciting process that might open new horizons in the world of digital assets and blockchain. In this article, we will review the main aspects of creating your own token: technical details, strategic planning, and legal nuances.
What Is a Token?
First, let me define what a token is in relation to blockchain. A token, in blockchain terminology, is an issue of some digital asset on a blockchain platform. Tokens can represent values ranging from virtual currency to pieces of assets or entitlements to some claimed service. Now, tokens come in several types, with the most common being utility, security, and governance tokens.
Platforms for Token Creation
You don’t necessarily need to be a professional developer to create a token. There are many services that will enable you to issue a token with a graphical interface or simple templates. Popular token creation platforms are Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Solana, and Tezos. The exact choice depends on what you intend to achieve, what security level is required, and what is expected from transaction speed.
Stages of Token Creation
Defining token purpose and functionality. First of all, you need to determine clearly what your token is going to be used for and what function it’s supposed to perform.
Choose the blockchain platform. According to your goals and technical requirements, decide upon a platform on which your token is going to reside.
Smart Contract Development. A smart contract is a program that controls the functionalities of a token on a blockchain network. To create a good smart contract, one needs profound knowledge in programming and should know how a given blockchain network works in general.
Testing. Before releasing a token, meaningful testing of a smart contract must be carried out to eliminate bugs and any kind of vulnerability.
Token Launch and ICO/IDO. After testing, issue your token and run an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) or Initial Decentralized Offering (IDO) to raise investment and attract users.
Legal Aspects
Designing and issuing a token involves legal risks. The law in which the token is to serve, or the country in which it is to be used, depends on different legislations and regulations. It is therefore recommended that any decision concerning the issuance of tokens must be done with consultations from legal experts dealing exclusively with blockchain and cryptocurrencies, so your token would not break the laws of your country, let alone international regulation.
What is Tokenomics?
Tokenomics or tokenomics model is the name given to the branch of cryptoeconomics that looks at economic systems based on blockchain technologies and their cryptocurrencies. This mainly deals with principles on the creation and distribution of digital tokens, which are units of value or access rights in a given blockchain system, and their management. The reason, therefore, is that token economics combines economics, finance, behavioral economics, and game theory in an effort to make continuous and efficient systems of digital assets.
Basic Elements of Tokenomics
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Tokens | Digital assets that run on the blockchain. The purpose of a token can vary from being a virtual asset—a type of cryptocurrency—to an access or voting mechanism within an ecosystem. |
| Supply and Demand | The driving force of token value is determined by its supply—the number of tokens in existence—and demand—the interest and purchasing power by users for them. |
| Token Distribution | Ways in which tokens are distributed to participants in an ecosystem, including initial coin offerings (ICOs), giveaways (airdrops), staking, and mining. |
| Consensus Mechanisms | Algorithms that maintain consistency in the data included in a blockchain for all participants. Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are examples that determine token distribution and incentivization directly. |
| Governance Rules | Rules and mechanisms by which the token ecosystem makes decisions, especially regarding changes to network rules, allocation of funds, or other important aspects of governance. |
Application of Tokenomics
Applications vary from finance and insurance to gaming and social networking. Tokenomics create economic incentives for the participants of the ecosystems by rewarding the desired behavior—for example, maintaining network security or participating in voting—and preventing undesired behavior. Probably the most interesting feature of tokenomics is the possibility of transparent and reliable economic relations without centralized regulation or intermediaries, which reduces costs and simplifies transactions.
What Programming Language to Use Creating Your Coin
It is a very complicated process that, with modern technology, has been made more available with the wide array of programming languages available for the wide array of programmers. Various different languages could be employed for creating a coin, but in fact, it depends on several factors such as blockchain platform, developer skills, and demands that have to be met by the project. Below are described the most usable programming languages regarding cryptocurrency creation.
| Solidity | C++ | Python | JavaScript | Rust |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solidity is the most popular language for creating smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. It allows developers to create complex decentralized applications (DApps), including ERC-20 and ERC-721 tokens. | C++ is used to create Bitcoin, providing high performance and security. It allows for control over system resources and memory, suitable for building blockchains. | Python is known for its readability and simplicity, making it a good choice for beginners. It can prototype cryptocurrencies and develop tools for blockchain interaction. | JavaScript is popular in web development and can be used to develop DApps that run in browsers, interacting with blockchains through libraries like Web3.js. | Rust focuses on security and speed, preventing common bugs. It’s used in projects like Parity Ethereum and Solana, suitable for building high-performance blockchain systems. |
Launch your own crypto token
Nowadays, it’s getting trendier to finance their projects using the blockchain technology startup and businesses by launching their crypto-token with a view to increase the transparency of operations and gaining new investors on board. In the context of such projects, Lithuania and the Czech Republic are two of the most sought-after jurisdictions due to an innovative approach adopted by local governments and a friendly regulatory environment, including the possibility to obtain a Crypto license in the Czech Republic.. The current article focuses on several key aspects and main steps toward launching a crypto-token, as well as some market peculiarities in these two countries.
Cryptotoken Launch
| 1. Defining the Token’s Purpose | Clearly define the token’s functionality: whether it will serve as a means of exchange, utility token for accessing services, or a security token for investment. |
| 2. Development of the White Paper | Create a white paper containing key project information, including technical details, economic model, team information, development plan, and security measures. |
| 3. Selecting a Platform | Choose a blockchain platform, such as Ethereum for ERC-20 tokens, to ensure compatibility and functionality. |
| 4. Legal Training | Ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, particularly concerning securities and consumer protection. |
Lithuania as a starting point for crypto tokens
Lithuania is a country with an open regulatory policy that hugely supports the innovative drive of crypto token creators:
- Regulatory clarity: The Lithuanian authorities are active in building up a very transparent environment for crypto businesses.
- Tax incentives: Lithuania provides one of the more attractive tax conditions for cryptocurrency businesses.
- Start-up support: It is known for its start-up support programmes and technological innovations.
There are the following advantages of implementing crypto token projects in the Czech Republic, too:
- Innovation environment: The Czech Republic has a very strong developer community with government support for technological innovation.
- Stable economy: The Czech Republic’s economic stability makes it an attractive destination for international investment.
- Liberal laws: Czech legislation on cryptocurrencies is reasonably liberal, making it easier to launch new financial products.
This turns Lithuania and the Czech Republic into a proper place for initiating crypto tokens, since their innovative and regulative approach is highly progressive, while at the same time, the economic environment of these countries is stable. At the eve of launching their crypto-token, it would be highly useful for companies to prepare an elaborated white paper, select a relevant technology platform, and follow the observance of all regulations in case of need. In such a way, they can make full use of the opportunities given by the two European countries.
Issuance of Stablecoins
Stablecoins are new cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets such as currencies or metals. The more they become one of the critical components of the latest emerging digital economy. Their stability and predictability, of course, offer an advantage not only in routine financial flows but also in more complicated financial structures. Considering European regulations, such jurisdictions as Lithuania and the Czech Republic provide better conditions for developing and issuing stablecoins. The current paper addresses the reasons why such countries are in demand as preferred jurisdictions for stackable coins in the light of their regulatory framework and economic and technological conditions.
Regulatory Environment
Lithuania
One of the most active fintech developing countries is Lithuania. It became one of the first European states to offer a clearly regulated regulatory environment for both cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies. The following points are being suggested by Lithuanian regulators:
- Clearly established permission requirements for conducting cryptocurrency transactions, such as the issuance of stablecoins
- The lowest possible tax rates for businesses involved in the use of cryptocurrencies
- Encouragement of innovation through government initiatives and funding of technology start-ups
Czech Republic
It is equally liberal with respect to the question of blockchain and cryptocurrencies. The authorities of the Czech Republic do not imply strict limitations for the operations with stablecoins, and that is a point of attraction for the fintech projects in the following respects:
- There is no specific regulation for stablecoins, so they are easy in their development and usage.
- Advanced financial infrastructure and technological ecosystem supportive of innovation in the sphere of digital payments.
Economic and Technological Framework
Economic Stability
The two countries ensure political and economic stability, which is the major motive in any long-term financial investment, and also to develop an infrastructure that would support a stablecoin. Economic stability gives a sound basis to the stablecoins especially those that are connected to the national currency.
Infrastructure of technologies
Excellent technological conditions to develop and test a cryptocurrency project are widely presented in Lithuania and the Czech Republic. It is about high-speed internet, highly developed IT infrastructure, talented IT professionals, hubs, and incubators that allow networking and collaboration among startups and investors.
However, Lithuania and the Czech Republic still offer outstanding opportunities to entrepreneurs willing to develop and issue stablecoins. Appropriate conditions of regulation, economic and political stability, and technological preparedness—common characteristics of both countries—make them enticing for those who would like to create innovations in the field of cryptocurrencies and use the potential of stablecoins for creating new financial instruments and services.
Creating New Crypto Currency
Creating a new cryptocurrency is an extensive process that needs tactical planning, a vast supply of technological resources, and profound knowledge of the regulatory environment. Lithuania and the Czech Republic is considered strong attractions for developers due to their innovative policy and business climate.
Defining the purpose and functionality
Before the release of the cryptocurrency, one needs to explain the very purpose and functionality. It might be a utility token intended to be used on a given ecosystem or cryptocurrency for wide circulation as a medium of exchange. The issues that are to be considered include the following:
- Target audience and users’ needs
- Economic model of the cryptocurrency: issuance and governance mechanism.
- The technology platform, for instance, on which the currency would be issued should be Ethereum for the issuance of ERC-20 tokens, for example.
Technology Infrastructure Development
To be able to create a cryptocurrency, a strong, secure technological infrastructure needs to be developed including:
- Select a blockchain platform: The selection can be one of an already developed blockchain platform or building your own.
- Development of Smart Contracts: Programming the contracts is needed to regulate the transactions, among other activities.
- Security: Develop measures to protect against hacker attacks and fraud in general.
- Regulatory aspects in Lithuania and the Czech Republic
Lithuania
One of the most progressive regulatory regimes for blockchain projects is implemented in Lithuania. For instance, the country established special economic zones for companies operating in the field of Fintech, which have enabled simplified access to financial markets and banking services.
- Licensing of cryptocurrency transactions: Clear criteria were established for obtaining licences, and this helped further new cryptocurrencies’ introduction.
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic has gained a reputation for being very liberal in the regulation of cryptocurrencies through providing an enabling environment for their development and use.
- Transparency in legislation: The laws of the Czech Republic have stipulated a relatively clear tax and legal framework for the cryptocurrencies, hence making it very attractive for a start-up in the cryptocurrency business.
And considering the innovative policy, highly developed technological infrastructure, and supporting regulatory climate of Lithuania and the Czech Republic, it would absolutely logically be claimed that the countries are among the most attractive jurisdictions for creating and launching a new cryptocurrency. Therefore, both countries may provide substantial advantages in terms of regulatory support and economic stability in turning them into the best option to consider for the registration of projects connected with developing and launching a new cryptocurrency.
Issuance of stablecoins in the EU
Interest in stablecoins has recently been on the rise. Stablecoins, for their part, are a sort of cryptocurrency pegged to stable assets like currencies or metals such as gold. That is why the role of these assets is a means for smoothing out the volatility which characterizes conventional cryptocurrencies. In the perspective of the European Union, certain countries, for example, Lithuania and the Czech Republic, are particularly noteworthy thanks to their progressive legislation and openness to financial innovation.
Lithuania: introduced new standards and supported innovation
Lithuania is considered one of the leaders in the European Union in developing a friendly legal environment to promote cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies. It has provided a very transparent legal structure for cryptocurrency transactions, and therefore, Lithuania became one of the favored countries for enterprises willing to issue and circulate stablecoins.
In 2020, the Bank of Lithuania issued a digital collection token, proof of its openness to new financial technologies and capabilities of the central bank in the digital economy. Besides, the government is active in enhancing legislation for protection of investors and increasing transparency of financial operations.
Czech Republic: stability and attractive tax conditions
 The Czech Republic is also very active in the field of cryptocurrencies and blockchain. In Europe, the most favourable conditions for cryptocurrency transactions exist within the Czech tax system, with no income tax imposed on certain types of cryptoasset transactions.
The Czech Republic is also very active in the field of cryptocurrencies and blockchain. In Europe, the most favourable conditions for cryptocurrency transactions exist within the Czech tax system, with no income tax imposed on certain types of cryptoasset transactions.
Czech legislation welcomes stablecoins as a form of payment, meaning more business opportunities. The government is very communicative and consults regularly with the industry to establish convenient and safe conditions for all market participants.
Prospects and potential challenges
Generally speaking, when considering the issuance of stackcoins in either Lithuania or the Czech Republic, there are some key aspects to be pursued. The first aspect involves a substantial review of regulatory requirements, which a company needs for complete compliance with the existing laws and regulations. The second important things will deal with the needs and expectations of the target audience and specifics of the chosen stablecoin.
Besides that, companies willing to capitalize on the opportunities in these countries should also be prepared for political and economic changes that may affect the state of the cryptocurrency market. The creation of a regular dialogue with local regulators and participants of this market is needed in order to build a sustainable and effective business model.
Of course, Lithuania and the Czech Republic open wide their doors to companies eager to issue and circulate stablecoins, given the support of innovation and appealing economic conditions. Success in this respect is impossible without thorough understanding of the local legislative framework, active engagement with regulators, and a clear market entry strategy.
Geography of Cryptocurrencies in 2024: Key Trends and Market Move Trends
Cryptocurrencies are featured to remain an important ingredient of financial systems all over the world. In 2023, cryptocurrency adoption has manifested in many interesting trends across regional and country contexts. Further, differences in regions impact both the institutional and retail segments of the market as cryptocurrencies maintain their relevance as a key lever against economic turmoil and digitization.
Key Trends:
- Leading countries in cryptocurrency adoption:India now ranks first in the world in cryptocurrency adoption, followed closely by Nigeria and Vietnam. Emerging markets are showing a high level of active users who use cryptocurrency for all types of everyday needs, from retail transactions to remittances. Even as the decline in cryptocurrency adoption in the wake of the collapse of premier platforms like FTX is still being felt, there has been a set of emerging economies that continues to show growth and recovery with consistency.
- North America: Regulatory Challenges and Institutional Investment:North America remains the biggest cryptocurrency market, accounting for 24.4% of all global transactions, totaling $1.2 trillion over the last 12 months. However, institutional activity has cooled since the bankruptcy of FTX and a subsequent banking crisis, reducing the usage of stablecoins and other crypto instruments. Retail remains quite active, especially in decentralized financial protocols.
- Latin America: Economic Crises and a Rise of Cryptocurrency Transactions:In Latin America, cryptocurrencies are active and used to protect against economic instability. Argentina and Venezuela lead the region in transaction volumes, with local populations using stablecoins to shield their savings from hyperinflation and currency restrictions. Argentina received a total of $85.4 billion through cryptocurrency transactions, making it the leading market in the region. This is how cryptocurrencies help residents of Venezuela sidestep the government’s restrictions and independently manage their funds.
- Europe: Increased Activity in DeFi and Institutional Investments:Central, Northern, and Western Europe remains the second-largest cryptocurrency market, with a total transaction volume of about $1 trillion. The region has seen increased use of decentralized financial services, mainly driven by institutional users. France, the UK, and Germany are some of the countries developing active legislative and regulatory initiatives to support institutional investments in both cryptocurrencies and DeFi.
- Eastern Europe: Impact of Conflict and Economic Instability:This also seems to explain why, despite economic sanctions and the effects of military conflict, Ukraine and Russia continue to use cryptocurrencies at high volumes. Transaction volumes are down in both countries, but the number of users remains the same. That means war and sanctions have further pushed the active use of cryptocurrency for everyday financial operations and transfers, particularly in the context of limited access to traditional financial services.
- Central and South Asia and Oceania: Leaders in Cryptocurrency Adoption:Over the last three years, India, Vietnam, and the Philippines have consistently been at the top in the ranking of cryptocurrency adoption in the world. In these countries, DeFi and P2P platforms can be markedly observed for the purpose of transactions and money transfers. The region has turned into a hotbed in the increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies to meet retail needs and crypto revenues on the basis of the play-to-earn model.
It is being analyzed that cryptocurrencies have been striking deeper and harder into the global market, mainly in those regions which are suffering from economic instability and inflation. In those developing countries, strong regulatory drives, more investments by any institutional entity, and innovative DeFi solutions are promising a very attractive future for further penetration of cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrency Trends 2024
- The Role of Stablecoins:Stablecoins have remained at the top in the global cryptocurrency market, mainly in those regions suffering from unstable economies. Indeed, Latin America and Africa come to be the most important regions of stablecoin usage for the protection of savings against local currency volatility and inflation. In particular, countries like Argentina and Venezuela are using stablecoins more actively to preserve their savings. In sharp contrast, in North America, stablecoin usage decreased because of the loss of confidence due to issues with crypto-friendly banks and the temporary loss of the USDC peg.
- The Rise of Decentralised Finance – DeFi:DeFi protocols are starting to play an increasingly bigger role in the global cryptocurrency ecosystem. In many regions, such as Europe and Asia, a big part of all transactions go through DeFi. Countries like France and Germany actively develop DeFi projects to bypass traditional institutes of finance and provide more free financial services. In Asia, institutional and retail customers widely use DeFi, which confirms the high adoption of this financial instrument.
- Activity on P2P Platforms:Within countries where more traditional financial services are scarce, P2P platforms are often the most vital way into cryptocurrencies. On a P2P platform, users can exchange cryptocurrencies directly with other users without the need to utilize a centralized exchange. Users operating in a more agile and cost-effective manner in their transfers and savings show a particular affinity for the use of P2P services.
- Institutional Acceptance of Cryptocurrency:Large institutional investors are increasingly entering the cryptocurrency market in advanced economies. In this respect, North America and Europe remain at the forefront of the trend. For example, in the UK, France, and Germany, the government and financial institutions are building favorable infrastructures for institutional investment in cryptocurrency by introducing licensing and regulations for cryptocurrency platforms.
- Regulatory Initiatives:Further regulation of cryptocurrencies is still very much in flux. The European Union codified common rules for all crypto-market participants into the MiCA Regulation. It resulted in increasing confidence in digital assets, which implied conditions for more transparency, risk mitigation, and further encouragement of institutional investments. Analogous work is being done with regard to legislation on a national level about cryptocurrencies within the United Kingdom, as well as in other European countries, which fosters stability in this fast-growing industry.
- Cryptocurrencies and Localised Economies:In states suffering from economic instability, cryptocurrencies became vital for the maintenance of economic activity. This happened—just to mention a few—in Venezuela as a way to circumvent the bond on currency; in Ukraine and Russia, they helped to sustain economic activity despite sanctions and war. In Argentina, it shields against inflation, and in Africa, it provides a foundation for cross-border remittances and micro-finance.
- Slowing Down the Global Adoption of Cryptocurrency:While cryptocurrencies remain a significant part of the global economy, there has been some deceleration in their adoption in recent years. This is due to the implosion of some major players like FTX and also because people are wary of this form of investing as a result of such collapses. However, in countries like India, Nigeria, and Vietnam, interest in cryptocurrencies remains high—a sign that they still play an important role when economies go bad.
In general, cryptocurrencies create huge impacts on the world economy by keeping crises and inflation at bay among developing nations. With growing institutional adoption, the development of decentralised finance, and new regulatory measures, there will be a sustainable environment for further growth in the cryptocurrency market for future times.
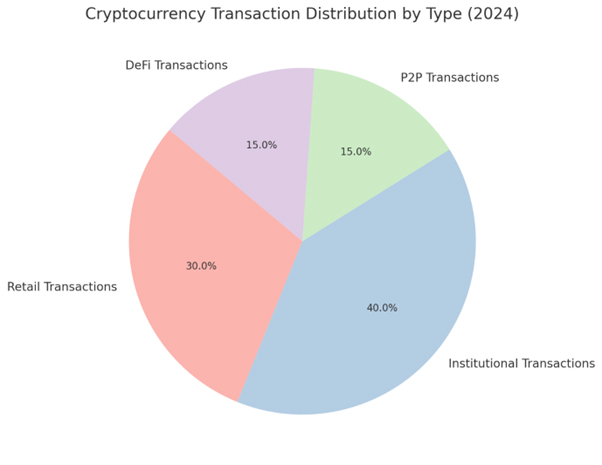
Chart showing the distribution of cryptocurrency transactions by type in 2024 (retail, institutional, P2P and DeFi).
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Can I create my own cryptocurrency?
Creating your own cryptocurrency is a resource-intensive process, both technically and legally. From a business point of view, cryptocurrency development opens a field of new opportunities in raising capital, internal transactions, and even unique financial ecosystems. It is necessary to especially pay attention to the legal side of the issue, as regulations may be different for various countries and natures of cryptocurrency use. Let's take a look at the key things one has to consider when creating their own cryptocurrency.
1. The Technical Aspect of Cryptocurrency Creation
Technically speaking, one can create a cryptocurrency using several methods:
- Designing Your Own Blockchain:This is very cumbersome and involves developing a blockchain protocol from scratch. A proprietary blockchain allows full control over the architecture and functionality of the cryptocurrency. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Creating a Token on an Already Existing Blockchain:This is faster and cheaper. Using blockchains like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or Solana allows the issuance of tokens via ERC-20 standards. Normally, this is done for the creation of tokens utilized in DeFi or ICO.
Whatever the road taken, designing a cryptocurrency is nevertheless a serious legal engagement regardless of the direction chosen.
2. Regulatory and Legal Aspects
Among the most daunting tasks facing developers of any new cryptocurrency are its legal design and compliance with the relevant laws. Every jurisdiction requires something different from these cryptocurrencies, and an inadvertently incorrect move in accordance with these regulations can lead to serious consequences, heavy fines, and the banning of activities in general. Major legal focuses include:
- Legal Status of Cryptocurrency:Cryptocurrencies are viewed differently in various countries, sometimes as assets, commodities, securities, or mediums of exchange. For example, in the US, tokens may fall under securities, necessitating registration with the SEC if considered an 'investment contract'.
- AML/CTF:Legislation around anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing should be followed in all jurisdictions where the cryptocurrencies are tradable. This necessitates Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures and transaction monitoring to prevent illegal financial transactions.
- Taxation:The taxation of cryptocurrency creation or sales should be acknowledged. Some countries treat sale proceeds from cryptocurrency as liable for income tax or capital gains tax. For example, in Germany, if cryptocurrency is held for less than a year, a capital gains tax is levied on the sale.
- Licensing and Registration:Depending on the specific type of cryptocurrency and its application, licenses may be required. If the cryptocurrency serves as a means of payment or participates in investment projects, registration must align with the corresponding payment system or investment platform's status.
3. International Legal Differences
A cryptocurrency for the international market should consider the differences in laws across countries:
- European Union:In this region, cryptocurrencies are regulated by law, such as MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation), which outlines clear rules about the issuance or trading of cryptocurrencies. Firms issuing or trading cryptocurrencies must comply with AML/KYC requirements and maintain transparency.
- US:In the US, the legal status of cryptocurrencies is overseen by authorities like the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) and CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission). Cryptocurrencies classified as securities fall under the respective requirements of the Securities Act.
- Asia:Countries like Japan, Singapore, and South Korea have legally adopted and regulated cryptocurrencies, recognizing them as acceptable means of payment. In contrast, China and India have taken a harsher stance, often banning or restricting cryptocurrency trading.
4. Business Opportunities and Risk Management
From a business perspective, creating your cryptocurrency opens many avenues:
- Fundraising through ICO/IEO:Initial Coin Offerings (ICO) were once popular for funding cryptocurrency projects but have largely been replaced by Initial Exchange Offerings (IEO). Both models involve selling tokens in exchange for investments from private investors before the platform goes live.
- Cryptocurrency Use in Ecosystems:Most projects create their cryptocurrency for use within their platform or ecosystem. Common applications of tokens include payment for services, content consumption, and voting in decentralized organizations.
- Risks:With opportunities come risks. Volatility in cryptocurrency exchange rates can negatively affect project liquidity. Additionally, legal uncertainties in various countries can lead to unexpected regulatory changes that might impact operations.
One can create their own cryptocurrency, but significant preparation is needed from both a technical and legal standpoint. Numerous legal issues must be addressed: regulation of cryptocurrency, taxation, AML and KYC compliance, licensure, and more. A proper legal strategy and adherence to regulations ensure sustainability and legitimacy for the project in the international market.
How long does it take to create a cryptocurrency?
Creating your own cryptocurrency is rather time-consuming, requires certain resources, and needs a vivid understanding of the legal and technical aspects of the question. The time required for creating a cryptocurrency depends on many factors: the complexity of the project, the chosen technology, its purpose, and whether it meets legal requirements. On average, development can take from several weeks to several months.
1. Technical Process of Making a Cryptocurrency
The period required for a cryptocurrency to be built may depend on the technical approach you use:
- Creating a Token on Top of an Existing Blockchain:For example, Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain: one to three weeks. Using standards such as ERC-20 or BEP-20 allows you to launch your token without developing your own blockchain. Major tasks at this stage include writing a smart contract, wallet arrangement, and testing security.
- Creating Your Own Blockchain:This is a more consuming method. The development and configuration of a new blockchain protocol may take three to six months, depending on complexity and required features. This includes writing code for a consensus algorithm, testing security, and setting up nodes for transaction validation.
- Security Auditing and Testing:Regardless of whether you create a token or a new blockchain, auditing code and security testing are essential. This might take another week to four weeks and involves testing smart contracts for vulnerabilities to prevent hacks or loss of funds.
2. Legal Procedures and Authorizations
Developing the legality of a cryptocurrency, especially for commercial use and an ICO/IEO, requires significant time. The process may begin with the following steps:
- Company Preparation and Registration:If you're creating a cryptocurrency for public use, the first step is registering the company. This may take one to two weeks, depending on the jurisdiction.
- Licensing and Permits:Some countries require you to obtain a financial license or register with securities regulators before launching your cryptocurrency. For example, in EU countries, compliance will be under MiCA regulations, while in the US, it may involve the SEC. The license issuance process typically takes one to three months.
- AML/KYC Compliance:Establishing an anti-money laundering program and user identification processes might take anywhere from four to six weeks for complete deployment and integration with the platform.
3. Raise Capital and Launch the Project
If the objective is to raise funds through an ICO or IEO, additional time is required for preparation:
- ICO/IEO Preparation:A white paper outlining the cryptocurrency's goals, token economics, and usage details must be written. Legal execution of this document typically takes two to four weeks.
- Marketing Campaign:For an ICO, effective promotion through social media, cryptocurrency forums, and specialized platforms is essential. Preparation and execution may take one to three months, depending on the scale and target audience.
4. Provide Legal and Compliance Support
Proper legal support is crucial at all stages of development and launch. This may involve drafting contracts, protecting intellectual property, and registering the company. Regular updates on cryptocurrency legislation are also necessary, especially for internationally focused projects.
5. Factors Affecting the Time Frame for Creating a Cryptocurrency
Several factors can influence the timeline for creating a cryptocurrency:
- Complexity of Technological Development: Complex consensus algorithms, smart contract support, or cross-chain integration may significantly extend development time.
- Jurisdiction and Legal Regulations: Countries with strict regulations require more time for obtaining licenses and permissions.
- Scale of the Project: Additional marketing and financial campaigns, such as ICO or STO, will also increase lead time.
- International Regulatory Differences: Launching a cryptocurrency in multiple countries will prolong the process due to varying legal regulations.
Creation can last from a few weeks to several months, depending on technical and legal aspects. Developing on an existing blockchain is quicker, while creating your blockchain and ensuring legal compliance takes longer. A cryptocurrency launch requires thorough preparation, from development and testing to legal compliance and security measures.
Do I need a licence to create cryptocurrency?
It is important to note that creating a cryptocurrency is not just a technical process but also a serious legal obligation, especially in adherence to the laws relevant to the country or jurisdiction where it will be launched. While the actual creation may not require a license, its use, distribution, and capital-raising activities fall under various regulatory mandates that may include licenses.
1. Creation and Status of Cryptocurrency
The process of creating a cryptocurrency, whether on your own blockchain or as a token on an existing blockchain (e.g., Ethereum), generally does not require obtaining permission. However, the crucial factor is how the cryptocurrency will be used and in which jurisdiction:
- Means of Payment:If a cryptocurrency serves as a means of payment for goods and services, this may trigger specific registration or authorization processes in certain jurisdictions. For example, operators of cryptocurrencies are regulated under the MiCA Regulation of the European Union.
- Transaction Platform:Establishing a platform for the exchange or trade of cryptocurrencies requires obtaining a license. In countries like the United States and the United Kingdom, operators of cryptocurrency platforms must acquire a digital assets license and adhere to AML requirements.
2. Compliance with Jurisdictional Requirements
Licensing requirements differ based on jurisdiction and the specific use of cryptocurrency. In some countries, the creation and issuance of cryptocurrency may be highly regulated:
- European Union:Under MiCA Regulation, the EU seeks to create a common legal framework for issuers and crypto-asset operators. If a cryptocurrency is used as a means of payment or involved in financial transactions, a license will be required under the national laws of the respective member state.
- United States:The legal status of cryptocurrency in the US is based on its use. Its issuance may require registration with the SEC if it meets the definition of 'security' under the Howey test. Licensing for cryptocurrency platforms and compliance with AML/KYC regulations must be managed by FinCEN.
- Asia:Countries like Japan and South Korea regulate the creation and use of cryptocurrency as digital assets and may require licensing as part of their payment systems. China has tightened its grip on cryptocurrency usage and trade within its borders.
3. ICOs and IEOs: Licensing Requirements
If planning an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) or Initial Exchange Offering (IEO) to raise capital, registration as an issuer is usually required:
- Registration as an Issuer:Most jurisdictions require the company issuing the tokens to register. This can complicate token issuance in the EU and the US, as it may be viewed as a securities offering, necessitating a license or registration with the authorities, like the SEC in the United States.
- AML/KYC Compliance:Crypto companies must comply with Anti-Money Laundering and Customer Identification norms during ICOs and IEOs, which include verifying investor identification before token sales and monitoring transactions to prevent illegal activities.
4. Licenses for Cryptocurrency Platforms and Exchanges
If the cryptocurrency's development is tied to launching a cryptocurrency or asset exchange, licensing is necessary:
- Financial License:In countries like Malta, Gibraltar, and Liechtenstein, cryptocurrency exchanges are required to obtain a financial license, akin to those held by banks or payment systems. This license allows them to process transactions, maintain customer accounts, and conduct exchange operations on their platforms.
- Investment Services License:For any investment projects involving cryptocurrency, such as Security Token Offerings (STO), an Investment Services License is required, governed by Securities and Financial Instruments Acts.
5. Legal Implications of Non-Licensing
Operating a business without a required license in jurisdictions where licensing is mandated can lead to serious legal consequences:
- Fines and Sanctions:Regulators can impose significant fines on unlicensed operators, sometimes amounting to millions of dollars, particularly for violations of AML regulations.
- Revocation:Operators without licenses may be forced to cease operations, with possible asset freezes and platform access being blocked or shut down.
- Criminal Liability:In some countries, such as China, developing or using cryptocurrency without permission can lead to criminal penalties, including imprisonment.
While the creation of cryptocurrency itself may not always require licensing, its use, sale, trading, and initial coin offerings often do. Compliance with licensing and AML/KYC regulations is essential for the legality and sustainability of a project, especially in international markets. Therefore, a serious approach must consider the legal requirements of the jurisdiction where the cryptocurrency is intended to be launched to avoid potential fines and sanctions.
What technical skills are needed to create cryptocurrency?
Creating a cryptocurrency is quite demanding in terms of technical skill, requiring advanced knowledge in programming, cryptography, blockchain technology, and network security. The task may involve either creating a new blockchain with unique features or issuing tokens on popular blockchains such as Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain. Here are the key technical skills necessary for successful cryptocurrency development.
1. Blockchain-Level Programming
The creation of cryptocurrency involves coding the underlying programming that dictates transactions, consensus mechanisms, and the economics of the system. A blockchain and smart contract developer should be familiar with a variety of programming languages:
- C++:This language is vital for developing blockchains, such as Bitcoin. It is necessary for low-level programming and when working with distributed systems.
- Python:Popular for blockchain application and tool development, Python is actively used in projects related to data analysis, automation, and testing.
- Solidity:This language is specifically used for creating smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, essential for developing Ethereum-compatible tokens or decentralized applications.
- Go (Golang):Used for blockchain and dApp development in Hyperledger and Ethereum, Go is suited for high-performance systems with effective multitasking capabilities.
Additionally, understanding consensus algorithms such as Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake, and Delegated Proof-of-Stake is crucial for resolving transaction validation issues and ensuring network security.
2. Cryptography
Cryptography is the backbone of digital cryptocurrencies and blockchains, securing transactions, creating digital signatures, and maintaining data confidentiality and integrity.
- Asymmetrical Encryption:Knowledge of public and private keys is foundational for digital signatures and secure transactions. Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) is commonly used in cryptocurrencies.
- Hashing:Cryptographic hash functions, like SHA-256 in Bitcoin, protect against data tampering. Understanding hashing is vital for both blockchain creation and network security.
- Protocol Cryptography:Familiarity with protocols that enable transactions without revealing comprehensive details is important, including Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP).
3. Functionality with Existing Blockchains
When creating a cryptocurrency on established blockchains, it’s essential to understand how these platforms operate:
- Smart Contract Writing:Implementing and testing smart contracts for token issuance and automation of business logic is crucial. On Ethereum, this involves standards like ERC-20 or ERC-721.
- dApps Integration:Designing and integrating decentralized applications (dApps) to interact with users and smart contracts is essential for user engagement.
4. Blockchain Technologies and Networks
A thorough understanding of decentralized network mechanics is necessary, including transaction validation and node construction:
- P2P Networks:Understanding how peer-to-peer networks function is crucial for blockchain operation, including node communication, block synchronization, and data integrity.
- Node Management:This involves initializing nodes and ensuring their proper functioning, including server management and network health monitoring.
5. Network Security and Risk Management
Developers must protect cryptocurrencies and blockchain networks from cyber-attacks, including DDoS, smart contract exploits, and phishing attempts:
- Smart Contract Protection:Testing smart contracts for vulnerabilities, such as reentrancy attacks, is critical. Security audits involve using specific tools to identify bugs and vulnerabilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication:Implementing security mechanisms like MFA in user wallets and interfaces helps protect against unauthorized access.
6. Testing and Deployment
Testing a cryptocurrency encompasses functionality, security, and compatibility aspects, which are essential before launching the project:
- Smart Contract Testing:Before deploying on the main network, smart contracts should be tested on test networks (e.g., Ropsten or Kovan) to identify potential issues.
- Network Load Testing:Testing network performance under high loads helps prevent scalability and transaction processing issues.
7. Integration with Cryptocurrency Wallets and Exchanges
A created cryptocurrency needs integration with wallets and exchanges to ensure usability and liquidity:
- Wallet Integration:Understanding the principles of wallets like MetaMask is crucial for successful integration.
- Exchange Listing:Skills in interacting with exchanges for listing tokens are essential for enhancing market visibility.
In summary, developing a cryptocurrency requires a wide array of technical skills, from blockchain programming to cryptography and network security. This comprehensive work demands necessary expertise at every stage, right from conceptualization to deployment.
Is it profitable to create your own cryptocurrency?
Creating your own cryptocurrency can be a profitable business project if approached strategically, considering every legal, technical, and economic aspect. With the growing popularity of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies, many companies and startups see opportunities in issuing tokens to raise capital, expand their business, and create digital ecosystems. For this to pay off, several factors are essential, such as community sustainability, an economic model, and a development plan.
1. Key Reasons to Create Your Cryptocurrency
There are several reasons why creating a cryptocurrency could be quite profitable:
- Funding through ICO/IEO:The primary goal of issuing your own cryptocurrency is to attract capital through an initial coin offering (ICO) or initial exchange offering (IEO). This allows companies and startups to secure investments during the early stages of project development without relying on traditional financial institutions. A successful ICO can raise millions in a short period, especially if it garners investor interest.
- Creating Internal Economies:Cryptocurrencies can help build an internal economy for platforms or enterprises. Companies can use their tokens to pay for services, manage decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), or develop reward systems for users, leading to lower costs and higher operational efficiency.
- Community Outreach and Development:Having a proprietary cryptocurrency can attract users and investors, fostering an active community around the project. Successful projects often rely on strong support from users interested in the ecosystem's development and growth.
2. Economic Model and Token Development
For cryptocurrency creation to be profitable, careful consideration of its economic model is crucial. Poor token management can lead to a drop in value and diminished investor interest.
- Tokenomics:Developing a balanced model of token utilization, known as tokenomics, is essential. Key aspects include:
- Total Supply: Scarcity can stimulate demand and increase value.
- Token Use: Tokens must serve a direct purpose within the network, such as payment for services, voting, or staking.
- Token Burning Mechanisms: Some projects implement token burning to reduce circulation and maintain high demand.
- Long-term Development Strategy: A comprehensive plan for ongoing development and platform expansion is vital for sustained demand and investor interest.
3. Community and User Engagement
A successful cryptocurrency project depends heavily on a strong, dedicated community of users:
- Role of Community:The community creates initial demand for tokens and contributes to project development through feedback and investment, often leveraging social media for promotion.
- User Adoption:Effective marketing campaigns, affiliate programs, and early investor incentives can drive interest and demand for the tokens. Successful projects utilize social media, forums, and crypto platforms to generate awareness.
4. Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Legal considerations can significantly impact the creation of a cryptocurrency:
- Status of Regulations Worldwide:The regulatory environment varies across jurisdictions. For instance, the MiCA Regulation in the EU addresses cryptocurrency issuance and trading, including AML/KYC requirements. In the US, cryptocurrencies may be classified as securities by the SEC.
- AML and KYC:Companies must verify user identities and monitor transactions, particularly when raising funds through an ICO or IEO.
- Licensing:Depending on the cryptocurrency's nature and use, registration may be required as a payment provider or digital asset operator in many jurisdictions.
5. Risks and Challenges
While creating a cryptocurrency can be lucrative, there are significant risks that may impact project success:
- High Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies often experience price volatility, which can lead to devaluation and decreased interest.
- Competitive Niche: The cryptocurrency market is highly competitive. Without a clear promotional strategy and unique offering, distinguishing a project can be challenging.
- Regulatory Changes: Sudden changes in legislation or increased regulation can pose challenges, particularly for projects targeting international markets.
6. Potential Benefits
If executed correctly, developing your own cryptocurrency can yield significant rewards:
- Capital Raising: Successful ICOs and IEOs can generate substantial funds for project development, facilitating growth and user onboarding.
- Token Value Increase: If a token maintains high demand and usage, its market price can increase significantly, benefiting creators and investors.
- Monetizing the Ecosystem: Many projects effectively monetize their tokens through platform management, transaction fees, or payment systems.
In conclusion, cryptocurrency creation can be profitable with a clear strategy, community support, and economic viability. However, success necessitates adherence to regulations, a thorough understanding of tokenomics, and effective risk management. A well-developed cryptocurrency can attract significant interest and generate substantial revenue.
RUE customer support team
RUE (Regulated United Europe) customer support team complies with high standards and requirements of the clients. Customer support is the most complex field of coverage within any business industry and operations, that is why depending on how the customer support completes their job, depends not only on the result of the back office, but of the whole project itself. Considering the feedback received from the high number of clients of RUE from all across the world, we constantly work on and improve the provided feedback and the customer support service on a daily basis.
CONTACT US
At the moment, the main services of our company are legal and compliance solutions for FinTech projects. Our offices are located in Vilnius, Prague, and Warsaw. The legal team can assist with legal analysis, project structuring, and legal regulation.
Registration number:
14153440
Anno: 16.11.2016
Phone: +372 56 966 260
Email: [email protected]
Address: Laeva 2, Tallinn, 10111, Estonia
Registration number: 304377400
Anno: 30.08.2016
Phone: +370 6949 5456
Email: [email protected]
Address: Lvovo g. 25 – 702, 7th floor, Vilnius, 09320, Lithuania
Registration number:
08620563
Anno: 21.10.2019
Phone: +420 775 524 175
Email: [email protected]
Address: Na Perštýně 342/1, Staré Město, 110 00, Prague
Registration number: 38421992700000
Anno: 28.08.2019
Email: [email protected]
Address: Twarda 18, 15th floor, Warsaw, 00-824, Poland
Please leave your request
The RUE team understands the importance of continuous assessment and professional advice from experienced legal experts, as the success and final outcome of your project and business largely depend on informed legal strategy and timely decisions. Please complete the contact form on our website, and we guarantee that a qualified specialist will provide you with professional feedback and initial guidance within 24 hours.