Inception of an Idea
However, history actually began long before the appearance of the first fully-fledged cryptocurrency named Bitcoin. In the 1980s and 1990s, scholars and cryptographers made attempts at inventing digital money that would be completely encrypted and secure for online use. One of the first harbingers was something called DigiCash, founded by David Chaum in 1989. Although DigiCash was not a commercial success, it was an important groundwork for the next generation of digital cash.
The Birth of Bitcoin
In 2008, someone, or a group, known as Satoshi Nakamoto issued a whitepaper describing the protocol, along with a working implementation of the Bitcoin currency. On January 2009, the first block, also known as the genesis block, was mined, which is considered to be the birthday of Bitcoin. This disruptive digital currency solved the double-spending problem, without resorting to a third party, and applied blockchain for added security.
Development and Take-off
Among the first cryptocurrencies to follow Bitcoin were Litecoin, which appeared in 2011, and Ripple in 2012. These so-called altcoins emerged with new ideas aimed at improving some characteristics of Bitcoin, such as its speed of transaction or/and energy efficiency. However, it was a landmark when Bitcoin first reached the price of $1,000 in 2013, an event which mobilized considerable public attention to the virtual currency market.
The Era of ICOs and Regulation
The crypto market has passed through such a boom of the ICO in 2017, when scores of new projects raised capital by issuing their own tokens. As a consequence, such activity has resulted in a jump of cryptocurrency numbers and unusual interest to this market by investors. The increasing popularity attracted fraudulent schemes, thus forcing governments to think about measures of market regulation.
Current State and Prospects
The modern cryptocurrency market is in constant development along the line of volatility and numerous challenges that are faced in legal regulations, among others, and technical ones. Besides financial applications, the blockchain technology has started to find adoption in various diverse sectors, starting with logistics and voting systems, but rather up to almost everything. Projects like Ethereum allow for the development of decentralized applications and smart contracts opening totally new possibilities.
The ever-growing number of debates concerning cryptocurrencies and blockchain draws a line to show their probable future participation in the financial system and further. Whereas some consider them to change everything, others, on the contrary, try to be reserved in their estimates by mentioning only risks and complications that may appear in the course of working with them. The history of cryptocurrencies is one of invention, trial, and scandal; it will no doubt continue to shape the future of the digital economy.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a medium of exchange that utilizes blockchain technology and cryptography for recording transactions and for control of the issuance of new units. As one subgroup of alternative digital currencies, the first decentralized cryptocurrency was Bitcoin, created in 2009. Since then, several other cryptocurrencies have been created. These are more generally called altcoins, short for alternative coins.
While the digital currencies employed in the centralized banking system are decentralized in nature, cryptocurrencies operate on a decentralized model. Decentralized control, for instance, in Bitcoin employs blockchain technology with records of transactions kept on a distributed electronic ledger.
With the high fluctuation in prices and increased fraud, financial regulators worldwide are attempting to put a limit or regulate cryptocurrencies and their services. Major advertising platforms like Google and Facebook are trying to set limits on advertisements related to digital currencies.
Units of cryptocurrency are created in the cryptocurrency network based upon a commonly known exchange rate, through some sort of calculation. Unlike centralized banking systems—such as the Federal Reserve or Central Banks—which control monetary supply through corporate boards or governments, cryptocurrencies operate independently. Satoshi Nakamoto created the original fundamental technical groundwork for cryptocurrency.
By 2024, there are hundreds of cryptocurrency specifications. Most of these specifications derive from Bitcoin. Independent participants, called miners, ensure security and integrity for cryptocurrency ledgers. Miners use their computers to verify dates and times of transactions and add them to a ledger. All these ledgers depend for their security on the assumption that the majority of miners behave honestly because of their economic incentives.
Key Attributes of Cryptocurrencies
According to PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), most cryptocurrencies share a set of the following characteristics:
- Tamper-resistant code.
- Mechanisms that avoid spending of units by users not owning them.
- Limited supply, though it is possible to create more units in subdivisions of existing units.
- Fast and irreversible value transfers via the Internet without financial middlemen.
- A decentralized network maintaining security and transaction verification.
- Internal mechanisms that self-sustain and incentivize the participation of new users by utilizing their computing power.
- Public transaction data kept in a worldwide public registry, similar to a general ledger.
- Personal security via a pair of public and private crypto keys.
- A core of developers and volunteers who maintain network stability and security.
In 1998, the computer engineer Wei Dai published a description of “b-money,” an anonymous distributed electronic money system. Later, the cryptographer Nick Szabo created an ancestor of Bitcoin entitled BitGold, which relied on individuals to complete proof-of-work functions to secure the currency.
Bitcoin is a first decentralized cryptocurrency that was developed in 2009 by an anonymous developer under a pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Digital currency used SHA-256 crypto hash function. Around 2023, approximately 19 million bitcoins are in circulation. The cryptocurrency Namecoin was developed to create a decentralized domain name system that prevented Internet censorship in April 2011. In October 2011, Litecoin forked into the first successful cryptocurrency to use a script other than SHA-256 for a hash function. Another well-known cryptocurrency is Peercoin, the first to adopt a hybrid consensus model of proof-of-work and proof-of-stake. Since many other cryptocurrencies emerged after the release of Bitcoin, few of them were able to succeed without considerable technical improvements.
There appeared more advanced, so called second-generation cryptocurrencies like Monero, Ethereum, Dash, and NXT for 2014 and onwards with support for address masking, smart contracts, sidechains, and asset creation.
Central bankers claim that the ever-growing use of cryptocurrencies—for example, Bitcoin—is drastically reducing their ability to influence the credit prices in the economy. The more popular crypto-trading becomes, the less confident consumers will be in fiat money. Gareth Murphy, a central bank official, has said, “Widespread recourse to cryptocurrencies would make the compilation of economic activity data more complex, as a preliminary step in conducting economic policy.” He considers virtual currencies to be a new challenge to the critical monetary and exchange rate policy functions of central banks.
On February 20, 2014, Jordan Kelly, founder of Robocoin, launched the first-ever Bitcoin ATM in the U.S. in Austin, Texas. It comes equipped with an identification document scanner for users. The Dogecoin Foundation, affiliated with the cryptocurrency Dogecoin, donated over $30,000 worth of dogecoin cryptocurrency to fund the Jamaican bobsleigh team at the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi, Russia.
As of the mid-2010s, many countries began to recognize cryptocurrencies as legal modes of payment in the course of transactions within the domestic territories.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency
 One of the advantages of cryptocurrencies is that their model eliminates a third-party financial institution from the process. For customers, cryptocurrencies offer fast and inexpensive settlements without any involvement of middlemen—just the transacting parties themselves, other than their internet service providers—and none of their personal information about themselves or the source of the funds. Transactions can, however, be traced by authorities if necessary, since there exists an equivalent to a general ledger known as the electronic public registry.
One of the advantages of cryptocurrencies is that their model eliminates a third-party financial institution from the process. For customers, cryptocurrencies offer fast and inexpensive settlements without any involvement of middlemen—just the transacting parties themselves, other than their internet service providers—and none of their personal information about themselves or the source of the funds. Transactions can, however, be traced by authorities if necessary, since there exists an equivalent to a general ledger known as the electronic public registry.
From a company perspective, cryptocurrencies are a low-cost means to conduct financial transactions. This is because of immediate settlement and minimized risk of refunds for disputed or fraudulent credit card transactions.
A survey by PwC reported that 81% of its respondents used cryptocurrencies to shop online, while 17% just like its anonymity. Other usages that garnered significant amounts are online gaming at 17%, and paying credit card debts at 14%.
However, the low liquidity of cryptocurrencies implies high costs in changing fiat money for cryptocurrency and vice versa. High price volatility of cryptocurrency also creates extreme risks for both consumers and businesses; hence, they are not very positions to hold for long periods.
Cryptocurrency Market Capitalisation
Bitcoin, for historical reasons, dominates at least 50% of the market capitalization of all cryptocurrencies. Other cryptocurrencies rise or fall depending on its value, which gets largely set by speculation in other limiting factors of the technology, known as blockchain rewards encoded in the Bitcoin architecture itself.
By mid-June 2021, cryptocurrencies are viewed as the highly unpredictable and volatile assets for the diversification of investment portfolios, but an opportunity like that is offered with some investment companies in the United States.
Legal Status of Cryptocurrencies
The legal status of cryptocurrencies is very different from country to country and in many countries is still undefined or in flux. In some countries, their use and trading is permitted, while in others it is prohibited or restricted. Various government agencies, departments, and courts classify Bitcoin differently. In China, after an ultra-fast adoption phase of cryptocurrencies in early 2014, the Bank of China also banned Bitcoin transactions. Initial cryptocurrency offering (ICO) transactions—an equivalent to an initial public offering—have also been outlawed in early September 2017 in China. A paper just published by academics at Oxford and Warwick also notes some features common to the precious metals market, and that Bitcoins offer something more than traditional currencies. Nations like Singapore, Australia, and Canada have issued or are in the process of issuing guidelines on how to handle cryptocurrencies, while the UK government has announced that it will begin legislating against criminal behaviour in relation to new types of currencies. On the international plane, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is considering financial crimes involving cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrencies also raise purely legal issues apart from any government policy. For example, there is a cryptocurrency called Coinye that was initially called Coinye West and adopted a logo of rapper Kanye West without permission, which is malicious trademark infringement, unfair competition, and cyberspace piracy.
Since the development of cryptocurrencies in 2009, there has been a growing demand and popularity, raising a number of speculations. Their unregulated use is speculated to provide some threat to society and the global economy. Others further speculate that altcoins could provide means through which anonymous crimes will be committed over the Internet. Some speculators hold that altcoin transactions, being independent of banks, can be used to help facilitate tax evasion. Because taxable income relies on an individual’s revenue, this will be very hard and, in a few cases impossible, to account for crypto transactions.
The networks are unregulated and anonymous, which is an aspect that many users love. Lack of regulation opens a window for perhaps potential criminals to attempt tax evasion and money laundering. Instead of operating through a complex web of structures and bank accounts offshore, the money laundering of altcoin takes place outside of institutions and can be done through anonymous transactions.
History of the First Cryptocurrencies
There was considerable hype about cryptocurrencies immediately after 2008, when Bitcoin was launched, but digital assets existed decades prior to the invention of BTC. The term “cryptocurrency” first appeared in 1989, when American computer scientist David Lee Chaum invented digital money. He used cryptography for protecting and validating transactions.
It wasn’t until the early 1990s that crypto methods and software were actually developed to cope with these problems, thus creating a fully decentralized electronic currency. In 1998, computer engineer Wei Dai published a paper where he introduced “b-money.” He discussed an anonymous distributed electronic money system.
Some even believe that the world’s very first cryptocurrency was called Bit Gold. Indeed, such currency did exist, and it was devised by blockchain pioneer Nick Szabo in the same year as b-money. Bit Gold was inspired by inefficiencies in the old banking system and a need to reduce the level of trust required for transactions.
None of these cryptocurrencies became official, but they inspire modern cryptocurrencies available to the market. First cryptocurrency: The first cryptocurrency is Bitcoin with the ticker BTC. It was developed by an anonymous programmer or a group of people under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. He wanted to create a decentralized alternative to the traditional financial system that was responsible for the global financial crisis in 2008.
Other new digital currencies have emerged and exist in the market since the creation of BTC, some basically emulating Bitcoin’s mission, others with completely different use cases. Ethereum, for example, is the second crypto asset by market capitalization and was launched in 2015 to create an ecosystem for decentralized applications and smart contracts.
Within the last decade, BTC went through multiple up-and-down cycles while the market was growing and maturing. Due to the extremely young age of this asset class, investor attitude towards it tends to change from time to time. Hence, the cryptocurrency earned the standing of a very volatile asset.
Why Did Cryptocurrencies Appear?
The biggest role of digital assets is to decentralize finances. Now, let’s see some pros and cons of cryptocurrencies.
Merits of Digital Assets:
- Proponents regard cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, as the money of the future and are trying to buy these currencies now, presumably before they will become more valuable.
- The fact that cryptocurrency does away with central banks, which over time tend to reduce the value of fiat through inflation, is a plus for some crypto-enthusiasts.
- To some, cryptocurrency is a promising springboard in communities who, until now, have fallen out of the traditional system. A Pew Research Center report from 2021 pegged Asians, blacks, and Hispanics “more likely than white adults to say they have ever invested in, traded, or used cryptocurrency.”
- Other users like the blockchain technology behind cryptocurrencies for the fact that it is a decentralized system for processing and recording data; it can also be safer than traditional systems of paying for goods and services.
- Some cryptocurrencies grant their owners the ability to gain passive income through a process called staking.
- Most cryptocurrency projects have not been tested, and blockchain technology in general has a ways to go before it is widely adopted. If the concept of digital assets fails to live up to its potential, then the long-term investor may never realize returns.
- Other risks also exist for short-term crypto investors: Virtual currencies’ prices tend to fluctuate very fast. That means that users can make money fast by buying assets at the right moment of time but also lose their investments by doing the same just before the crypto market collapses.
- Great ecological footprint created by Bitcoin and projects based on the Proof-Of-Work consensus algorithm. For example, research done by Cambridge University estimated that BTC mining consumes more than twice as much electric power as all residential lighting in the United States. There are, however, some cryptocurrencies that make use of another technological choice and require just minimal energy, called Proof-Of-Stake.
- Governments around the world have not yet fully decided how to treat cryptocurrencies, so regulatory changes and restrictions could affect the market in unpredictable ways.
First Altcoins
Cryptocurrencies that have emerged after BTC are called altcoins. Most altcoins try to address the shortcomings that Bitcoin has and come up with competitive advantages in new versions.
The word “altcoin” is a combination of two words: “alt” and “coin,” in which alt stands for “alternative,” while coin simply relates to a cryptocurrency. Altogether, it refers to any type of cryptocurrency that is considered to be an alternative to a digital currency entitled Bitcoin. After the successful establishment of Bitcoin, several other peer-to-peer digital currencies were launched that tried hard to mimic the success of BTC.
This structure embedded in Bitcoin is further utilized to build many altcoins. Hence, most such assets are peer-to-peer and use PoW. However, altcoins, though having many similar characteristics, are quite different from each other.
Let’s look into some of the oldest cryptocurrencies that were launched after Bitcoin:
- Litecoin (LTC): Litecoin was forked in October 2011 by Charlie Lee and was supposed to be a speedier version of Bitcoin, considering block confirmation time, as well as using a different hashing algorithm.
- Namecoin (NMC): Namecoin launched in April of 2011. It provides a decentralized manner with which to perform domain name registration. With Namecoin, anyone is in a position to own their domain name with no help from third-party registrars.
- Peercoin (PPC): It was released in August of 2012 and introduced a unique PoS consensus algorithm that secures the transactions and guarantees security for the network. It differed from BTC in this regard.
- Ripple (XRP): Launched in 2012, Ripple was meant to be a digital payment protocol that can conduct cross-border transactions instantly and securely. Its consensus algorithm involves a network of validators rather than actual mining.
The creation of Bitcoin
The story of Bitcoin starts way before it was actually invented, in a time when the concept of digital cash had been floating around for quite some time. For decades, scientists and cryptographers tried to enable secure digital currency. Projects such as b-money by Wei Dai and Bit Gold by Nick Szabo proposed ideas very similar to what would later be part of the foundational base of Bitcoin, but they remained only theoretical.
In October 2008, an unknown entity or group of people under the alias Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper entitled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” It described a currency that operates independently and needs neither blind faith in some central authority nor intermediaries to guarantee the integrity of transactions. Satoshi envisioned a system utilizing blockchain: a highly decentralized transaction database administered by a network of nodes.
In January 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto mined the first Bitcoin block, called a genesis block, and from that moment Bitcoin began to exist. Since then, Satoshi and early members of the network have begun to use Bitcoin and improve it; he discussed it in forums and crypto mailing lists.
Initially, Bitcoin possessed no value in conventional currencies, and the first transactions had more of an experimental nature. Probably the most historic moment was that two pizzas had been purchased for 10,000 BTC in May 2010; it is now considered one of the first real uses of Bitcoin as a medium of exchange.
Satoshi Nakamoto remained active in the development of Bitcoin until late 2010 and then handed over the management of the project to Gavin Andresen, after which he disappeared, leaving many unanswered questions concerning his identity and motives.
After Satoshi’s departure, Bitcoin gradually attracted a lot of attention, its value started to rise, inviting investors, speculators, and unfortunately many criminal freaks who saw it as a means to money laundering and other illegal transactions, including the purchase of so-called services on the dark web such as Silk Road.
Amidst all the negative press, Bitcoin gained momentum as an alternative to traditional financial systems and especially in overall financial crises when people were looking for more stable stores of value.
With time, Bitcoin and the blockchain became understood as not only an investment tool but also as the way to create new ground for financial and technological inventions. Further development related to smart contracts, DeFi, and NFT made it obvious that what is possible on the blockchain surpasses by far the limits of any ordinary means of exchange.
This is a story of innovation, mystery, and inevitable challenges that unfolded in the creation of Bitcoin. The digital currency has survived skepticism and opposition against it, but it grew to be one leading cryptocurrency, which continues to inspire the rise of new technologies and alter overall perceptions of the financial system. While this still remains a very highly debated topic, it’s hard to deny that Bitcoin has left an indelible mark in the history of finance and technology.
Bitcoin history in numbers
Nakamoto developed the first block in the network of bitcoin in January 2009. It is also called the “genesis block” or “block #0”. The history of BTC starts from here. Bitcoin had no practical value in its early days and was used basically to test the network, showing the workability of blockchain technology. But as time passed, peoples’ awareness about bitcoin and its potential started raising one after another.
In 2010, the first bitcoin exchange was opened, Bitcoin Market, and for the first time, the bitcoin exchange rate was set: 1 bitcoin approximately cost 0.003 USD. In the same year, the first real purchase in bitcoin was made: user Laszlo Hanech bought two pizzas for 10,000 BTC.
Bitcoin started to grow in popularity and also to attract increasing attention in the beginning of 2011. The attention was hugely driven by Silk Road, an anonymous marketplace on the “dark side” of the Internet where bitcoin is used as a means of paying. Because of this, the demand for bitcoin increased; hence, its value gradually increased.
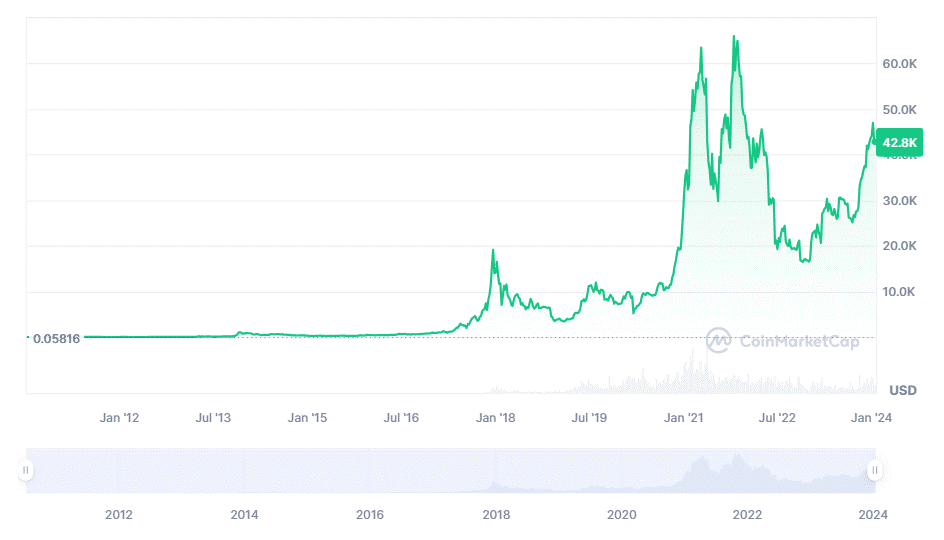
Back in 2013, 1 BTC passed the $100 price. In November of the same year, it first reached $1000. At this time, serious investment flow into the bitcoin industry started to take place, and new cryptocurrencies were emerging.
In 2014, the lull happened-the price of bitcoin significantly went down due to a number of problems, including those of Mt. Gox major exchange hacks. By 2016, BTC recovered and continued to grow until it strengthened its position of the world’s cryptocurrency leader.
From 2017 to 2018, bitcoin ran the gamut from incredible highs to incredible lows. In December 2017, it reached an all-time high, breaching more than $19,000 per unit. However, after that, there was a sharp drop in its graph, and by the end of 2018, it had gone down to US$ 3,000.
Starting in 2019, after the sharp decline in prices in 2018, bitcoin started to recover. The key trends this year included increased interest from institutional investors, the adoption of bitcoin as a means of payment by leading technology companies, and growing acceptance by regulators all over the world. At the end of 2019, the price of the first cryptocurrency had recovered to ~$7,000.
The year 2020 was pretty special for BTC. It was the year of the halving, something that happens every four years and cuts by half the reward for mining new blocks. The halving leads to less supply of new bitcoins, something that at least in theory can bring higher prices. Besides, due to the current global COVID-19 pandemic, a kind of global economic crisis has been triggered, and many investors have turned to bitcoin for “digital gold”-a hedge in case of uncertainty. By the end of 2020, the price of bitcoin had broken through its previous record and reached $20,000.
In 2021, the price of bitcoin continued higher and set a new all-time high several times. Large investments in bitcoin by companies such as Tesla, which also announced that they would accept it as a means of payment, gave BTC the status of the world’s leading cryptocurrency. Besides, several bitcoin-ETFs had been launched by that time, which gave institutional investors an opportunity to get into BTC more easily. In October 2021, the price of bitcoin finally broke the $60,000 level.
In 2022, the bear cycle started when the price of BTC dropped to $16,000.
By the middle of 2023, the bear cycle is slowly ending with the next halving, coming of big investment funds into the crypto market. Moreover, the appearance of stricter regulatory measures in different countries led to further development of the cryptocurrency ecosystem and increase of transparency.
Today, bitcoin is active in investment, speculation and, in some cases, in real transactions. It has influenced not only the financial sphere but also serves as a driver for new technologies and concepts like blockchain and decentralized finance.
Bitcoin price 2012 – 2024
Blockchain history
The history of blockchain is not all about Bitcoin or related cryptocurrencies. In fact, as early as 1991, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta made the first proposal for a kind of distributed ledger that had no need for a central governing body. Their work, aimed at making a system that could store time-stamped documents unalterably and untamperably, was to form the bedrock of future developments in blockchain.
Bitcoin and the first practical blockchain
In 2008, a person or group of people under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper describing a digital currency called Bitcoin and its main constituent, blockchain. It was the first pragmatic use of blockchain-a decentralized, distributed registry of all transactions recorded in the Bitcoin network. The idea here for achieving consensus in this decentralized network was proof of work, which made it safe and secure.
Extending Blockchain Capabilities
The success of Bitcoin increased attention to blockchain drastically. The other potential uses of the tech behind cryptocurrencies were explored by developers and researchers. In 2013, Vitalik Buterin proposed the making of Ethereum-a platform that would extend the uses of the blockchain via “smart contracts.” These self-executing contracts, encoded in the blockchain, allowed for automated execution of an agreement without using any intermediaries; thus, the building of decentralized applications was born.
Blockchain beyond finance
Since then, blockchain applications have extended to cover logistics, healthcare, identity, real estate and many other diverse fields. Several companies and governments around the world started exploring blockchain applications with the goal of making their operations transparent, secure and effective. For example, supply chain blockchain can track where goods came from and guarantee their genuinity, therefore avoiding counterfeiting.
Issues and challenges
This technology, while holding great promise, has a number of serious challenges, notably scalability, energy consumption-in particular, proof-of-work systems-and data privacy. Overcoming these challenges is the subject of energetic research and development work in cryptography and information technology.
The future of blockchain
With continuous innovation and research to surmount existing challenges, the future indeed looks brilliant for blockchain. The second- and third-generation technologies, such as the Lightning Network development on top of Bitcoin and Ethereum’s scaling solutions, promise to make blockchains mainstream, easy, and suitable for a wide range of applications.
So, blockchain history is one of those continuous changes and innovations pursued unabatedly to find new ways of using the technology for a more secure, open, and fair digital future. From a simple mechanism that backs cryptocurrencies to a bedrock upon which a new generation of internet technologies is laid on, blockchain keeps rewriting the way we interact and conduct business on a global scale.
History of blockchain by year
1991-2008: The early years of Blockchain Technology.
Which is the origin of blockchain? Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta came up with what many people referred to as blockchain back in 1991. Their earliest work involved working on a crypto secure blockchain where nobody could tamper with the time-stamps of any document.
In 1992, they updated their system to introduce Merkle trees that allowed efficiency gains, enabling the collection of more documents on a single blockchain. The real beginning of this story, in terms of relevance, though, starts in 2008 at the hands of one person or group of people using the name Satoshi Nakamoto.
Satoshi Nakamoto is considered to be the brain behind blockchain technology. Little do people know about Nakamoto; one belief is that he was the man or group of people working on Bitcoin, which was itself an application of the first-ever digital ledger.
Nakamoto conceptualized the first blockchain in 2008, from where the technology evolved and found its way into many applications beyond cryptocurrencies. Satoshi Nakamoto released the first white paper on this technology in 2009. In that white paper, he explained in great detail how, given that with the aspect of decentralization no one would ever control anything, the technology was well equipped to increase digital trust.
Nakamoto conceptualized the first blockchain in 2008 from where the technology evolved and found its way into many applications beyond the cryptocurrencies. Satoshi Nakamoto released the first white paper on the technology in 2009. He explained in the paper how the technology was well equipped to increase digital trust due to the decentralization aspect, which means no one would ever control anything.
Blockchain structure
In other words, a blockchain is a distributed peer-to-peer ledger that is secured and used to record transactions across many computers. The contents of the ledger can only be modified by the addition of another block linked to the previous block. It can also be thought of as a peer-to-peer network running on top of the Internet.
From a business or layman perspective, blockchain is no more than an enabling platform on which people are allowed to do any transaction without the need for a central or trusted arbiter.
The created database is shared transparently among members of the network in such a way that any person can see its contents. Each database is autonomously managed through peer-to-peer networks and a time stamp server. Information within the blockchain is organized in such a way that each block refers to the content in a previous block.
The blocks that make up a blockchain carry sets of transactions agreed upon by the participants of the network. Each block has the crypto hash of a prior block in the chain. Learn more about what a blockchain is.
Blockchain technology
In 2008, the application of blockchain came as Bitcoin. Satoshi Nakamoto had described it in his white paper as an electronic peer-to-peer system. Nakamoto formed a genesis block; during the mining process, other blocks that were linked to it were mined, thus resulting in one of the largest blockchains that carry various information and transactions.
Since Bitcoin, the blockchain application, went live, a lot of applications have emerged that tend to utilize the principles and capabilities of digital ledger technology. The history of blockchain therefore contains a long list of applications which have emerged with the development of this technology.
Living in a world where innovation is literally at the door of the day, Vitalik Buterin is among those on the list of developers who feel Bitcoin has not arrived at the juncture where it can utilize the full potential of blockchain technology.
Due to these limitations of Bitcoin, Buterin started working on a blockchain that he thought would be flexible, from merely being a peer-to-peer network performing a variety of functions. Ethereum came into existence in 2013 by the development of a new public blockchain with functions that allowed it to be used for many more things than just store money, unlike Bitcoin. It was this very development that turned out to be a turning point in blockchain history.
Going back, Buterin had differentiated Ethereum from the Bitcoin blockchain by the inclusion of a feature that allowed people to record other assets, such as slogans and also contracts. In any case, the new feature expanded Ethereum’s functionality from a cryptocurrency to a platform for developing decentralised applications.
Officially launched in 2015, the Ethereum blockchain has grown to be one of the largest applications of blockchain technology, taking into consideration the fact that it can support smart contracts for the performance of various functions. The Ethereum blockchain platform also managed to gather around an active developer community that has created a real ecosystem.
Ethereum blockchain supports smart contracts and decentralized applications; hence, it processes the most significant number of transactions daily. In the cryptocurrency space, its market capitalization has also gained considerably.
However, Ethereum and Bitcoin are not all there is in the history and development of blockchain. A number of projects have recently used blockchain to its full capabilities. New projects have been the solution to some of the shortcomings with regard to Bitcoin and Ethereum in addition to other new features that take advantage of the capabilities of the blockchain.
NEO belongs to the category of newly developed blockchain applications. It was proclaimed to be the first open-source decentralised blockchain project launched in China. Despite the fact that this country has banned cryptocurrencies, it still is active when it comes to blockchain innovation. NEO, on the other hand, is positioning itself as China’s Ethereum and already attracted support from Alibaba CEO Jack Ma with plans to make a similar impact as Baidu in the country. In the race to fast-track the development of the Internet of Things, some developers utilized blockchain technology, and in the process came up with IOTA. The cryptocurrency platform is optimized for the Internet of Things ecosystem because it offers zero transaction fees and unique verification processes. Some scalability issues associated with Blockchain1.0 Bitcoin are also discussed.
But apart from IOTA and NEO, a long list of second-generation blockchain platforms is making waves in the nook and corner of the sector. The blockchains of Monero Zcash, and Dash have emerged as a way to solve some of the major security and scalability issues that were associated with early applications of blockchain. Thus, they have been named Altcoins; these blockchain platforms make efforts to present a high level of privacy and security in transactions.
The above blockchain story discussed a publicly available blockchain network, where everybody has access to its contents. However, as the technology began to evolve, a number of companies started to adopt it internally in order to enhance operational efficiency.
Large enterprises are investing heavily in hiring specialists, wanting to get ahead in leveraging the technology. Other firms, like Microsoft, appear to have already taken the lead in investigating uses of blockchain technology, which have come to be known as private, hybrid, and federated blockchains.
Blockchain programming
In 2015, the Linux Foundation proposed the opensource blockchain project to Umbrella. They kept naming it Hyperledger which to date has served as a Distributed Ledger development collaborative. Under the leadership of Brian Behlendorf, the focus of Hyperledger is to bring cross-industry collaboration in blockchain and Distributed Ledger development.
Hyperledger’s key focus is to develop the adoption of blockchain technology to accelerate the performance and trustworthiness of current systems in support of business transactions worldwide.
EOS was the brainchild of the private company block.one that came into being in 2017 when a white paper was published, describing a new blockchain protocol that was powered by EOS as its native cryptocurrency. Unlike other blockchain protocols, EOS attempts to emulate many of the attributes of real computers, including CPUs and GPUs.
Due to this, EOS.IO becomes both a smart contract and decentralised application platform. It is actually trying to enable the deployment of decentralised applications with an autonomous decentralised corporation as an incentive.
The future of blockchain technology is shining so well partly because the governments and businesses are putting heavy investments in an effort to drive innovation and applications.
With each passing day, it is becoming crystal clear that there is going to be a public blockchain that everybody is going to use. Proponents of blockchain expect the technology to help automate most tasks performed by professionals in all sectors. Already, the technology is finding extensive use in supply chain management as well as in the cloud computing business. In future, the technology should also find use in basic elements such as internet search engine.
Gartner Trend Insights estimates that at least one blockchain business will have a value of over $10 billion by 2022. As the technology is yet in its development phase, the value to be provided by businesses owing to the growth of digital ledger technology is estimated to cross over $176 billion by 2025. And by 2030, according to research, it will be worth over $3.1 trillion.
Investments in cryptocurrencies
During the past couple of years, the investing in cryptocurrency was widely adopted by a wide audience among investors due both to great opportunities for profit and unique risks. The following article is aimed at an overview of the cryptocurrency market, the necessary understanding of its basis, and investor’s risk management.
Cryptocurrency Basics
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies or virtual currencies that make use of cryptography for security, controlling the creation of new units. Bitcoin was the very first cryptocurrency, which was introduced in 2009 and is the most recognized and largest by market value to this date. In fact, since its inception, thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies called altcoins have been created, each with their own features and uses.
Why Invest in Cryptocurrencies
| Reason | Description |
| High Yield Potential | Some of these digital currencies have been seen to increase in value exponentially, hence yielding high returns to investors. |
| Portfolio Diversification | Digital currencies are not highly related to traditional financial assets. Because of this, they can be a good tool in diversifying any portfolio. |
| Funding Innovative Financial Technologies | A chance to invest in a new financial technology and decentralized applications is given by investing in cryptocurrencies. |
Risks of Investing in Cryptocurrencies
| Risk | Description |
| High Volatility | Depending on specific conditions, virtual currency prices highly increase and decrease. In this respect, it presents broad opportunities and risks for investors. |
| Regulatory Uncertainty | Because of the constant development of legal status, changes in regulations might influence the market in the future. |
| Technological and Operational Risks | Security issues, hacker attacks, and loss of wallet access can lead to an inability to use the funds. |
| Market Manipulation | In smaller markets that are not well-regulated, price manipulation is easier. |
Risk Management Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
| Diversification | The risk factor can be brought down by investing in a variety of cryptocurrencies along with other asset classes. |
| Cautious Investing | Invest only the amount that one can afford to lose. |
| Research and Education | Research the market, technology, and specific cryptocurrencies constantly before making the investment. |
| Use Trusted Platforms | Only trusted and reliable platforms must be used to trade and store the cryptocurrencies. |
| Long-term Investing | Given the future growth potential of the cryptocurrencies, it will be prudent to consider them as a long-term investment. |
Investment in cryptocurrencies has provided unparalleled opportunities and risks. The savvy investor cautiously approaches the market, grounds decisions on sound research, and manages risk. With the proper approach, crypto can be a real value add to any investment portfolio because of the diversification potential and the possibility for exceptionally high returns.
What is crypto trading?
Trading in cryptocurrencies has become one of the most preferred modes of investment and returns in this digital era. From the invention of Bitcoin in 2009 to the development of thousands of altcoins afterward, the market became a playing field for speculators like never before. This paper reviews crucial aspects of cryptocurrency trading: strategies, risks, and best practices.
Cryptocurrency Trading Basics
Cryptocurrency trading consists of buying and selling digital currencies at exchange platforms with an eye towards gaining from fluctuations in their values. High market volatility, around-the-clock trading, and openness to traders from every corner of the globe are the most attendant advantages of cryptocurrency trading.
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Cryptocurrency trading strategies | Long-term investing (HODLing): This strategy involves buying a cryptocurrency for a long period and holding it based on belief in its long-term growth. Day trading: A short-term trading strategy where buyers sell cryptocurrency within one day to capitalize on short-term price changes. Swing trading: This approach captures medium-term trends and fluctuations in prices, typically lasting several days to weeks. Scalping: An extreme short-term strategy where traders attempt to profit from small price changes by executing a large number of trades in one day. |
| Risks of trading in cryptocurrency | Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are prone to sudden price changes, which can lead to significant gains or losses. Regulatory risks: Different treatment by governments and regulators affects the value and legality of cryptocurrencies in trading. Security: Hacker attacks on exchanges and wallets pose a substantial risk of monetary loss. Market manipulation: A small market size and minimal regulation contribute to manipulation and arbitrage. |
| Best practices of cryptocurrency trading | Education and Analysis: Continuous study of the market, chart analysis, and staying updated with news help in making informed decisions. Risk Management: Employ risk management strategies, such as stop-loss orders, to protect against significant losses. Diversification: Avoid putting all your investments in one asset. Diversifying across asset classes can mitigate key risks. Mental preparation: Trading cryptocurrencies requires discipline and composure. Avoid emotional decision-making and adhere to your trading plan. |
Cryptocurrency trading has great opportunities for profit, but it has great risks. Success requires in-depth market knowledge, strict discipline, and effective risk management. Novice traders should begin to trade cautiously, investing only the amount that they can afford to lose.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain, the innovation behind the fascination with virtual currencies like Bitcoin, is perhaps one of the most hyped technologies of the last ten years. Its principles and possibilities go way beyond financial applications and promise to radically change many industries-from banking to supply chains. In this paper, we will plunge into the very understanding of what blockchain is, how it works, and what prospects it holds.
Strong Features of Blockchain
- Decentralisation: Unlike most other databases, which are centrally controlled, blockchain is distributed among all the participants of the network. It thus reduces the risk of centralized failures and attacks.
- Transparency: Though participants can remain anonymous, all transactions are open to all members of the network. So, it is quite transparent at a high level of generality.
- Immutability: Data added to the blockchain cannot be modified without changing all subsequent blocks and gaining the consensus of the greater part of the participants in the network. • Censorship-resistant: Blockchain ensures that data cannot be unilaterally altered or deleted. Applications of Blockchain
- Cryptocurrencies: The most well-known use of blockchain is to create and manage digital currencies, such as Bitcoin.
- Smart Contracts: Enforceable contracts with their terms directly written in the blockchain add to the security and reduce reliance on middlemen.
- Supply chains: Blockchains can offer complete transparency of the origin of goods and track their flow from producer to consumer.
- Identification: It provides a secure and immutable method of verification of identity and achievements.
- Voting: It has a potential application in providing secure and genuine ballot systems.
Issues and Perspectives}
However, blockchain in itself comes with its own set of obstacles, ranging from issues related to scalability, problems regarding energy consumption, to even regulatory problems in blockchains that possess Proof of Work protocols. Nevertheless, ongoing research and development efforts are aimed at overcoming these obstacles, paving the way for wider acceptance and application of the technology in various spheres of life.
Blockchain offers an innovative approach to recording data securely and transparently that has the potential to radically change many industries, from finance to data management. As the technology continues to evolve and improve, we can expect to see it increasingly used in our society.
Cryptocurrency with highest value
The cryptocurrency market is one of the biggest wonders that attracts investors and enthusiasts alike from around the world. Among thousands of cryptocurrencies available, some stand out due to their high market capitalization, which is indicative of investors’ confidence in the currency and their appreciation of the potential thereof. In this article, we present an overview of the largest capitalization cryptocurrencies, their features, and importance to the market. The list starts with the following:
 Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin is undoubtedly the leading cryptocurrency in terms of market capitalization. Created in 2009 by a developer, or a group of developers under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin gave the world an opportunity to get acquainted with such a thing as blockchain and a decentralized digital currency. Moreover, it remains the most recognized crypto and often serves as an “entry gate” for new entrants into the cryptocurrency market.
 Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum takes second place in the market capitalization ranking and is a platform for building DApps and smart contracts. Its flexibility and large possibilities for programming have made Ethereum the backbone of a great number of projects in the sphere of DeFi and NFTs.

Binance Coin (BNB)
Binance Coin is the utility token of the Binance exchange, which is one of the most extensive cryptocurrency exchanges in the world. It was initially launched on the Ethereum blockchain and recently moved to its own blockchain, Binance Chain. The token has a number of advantages on the exchange: paying for commissions using it grants a discount, the token is used to participate in token sales, and works as a medium of exchange within the Binance ecosystem.
 Cardano (ADA)
Cardano (ADA)
Cardano is a blockchain oriented toward security and sustainability by means of a multi-layered architecture. The project is designed to be scientifically and formally verifiable from the code, which makes it one of the most interesting projects in the area of developing decentralized solutions and smart contracts.

Ripple (XRP)
Ripple also attempts to help international payments and make them cheaper with its token XRP. Unlike most cryptocurrencies, Ripple concentrates its efforts on collaborating with banks and financial institutions, offering them a fast and reliable alternative to traditional methods of settlements.
Market Capitalisation: Trust Indicator
Market capitalization is a major indicator of investor confidence in cryptocurrency and also is a reflection of the overall value the market attributes to the cryptocurrency in question. It could be calculated by multiplying the current token price by the total number of tokens in circulation.
Large capitalization cryptocurrencies continue to head the market of proposals for new financial and technological solutions. Their success and popularity prove that cryptocurrencies are becoming a substantial part of the modern economy and investment landscape. Even though the cryptocurrency market is still volatile, these currencies can show the potential of the blockchain to change the world we live in.
What is ERC-20?
ERC-20 is a general standard applied to all smart contract tokens for the Ethereum blockchain; this abbreviation means Ethereum Request for Comments 20. In 2015, a proposal was submitted by Fabian Vogelsteller and other participants in Ethereum. This has been a basic standard to create and publish tokens within the Ethereum network. It covers the general rules to which all tokens used on the network should adhere. In such a way, it ensures their compatibility with one another and with various contracts and applications-wallets and exchanges in particular.
Main Features of the ERC-20
ERC-20 defines six obligatory features that need to be implemented in a token, plus three optional features:
- totalSupply: Returns the total amount of tokens that are in circulation.
- balanceOf: Returns the number of tokens that belong to an address.
- transfer: Allows you to transfer tokens from one address to another.
- transferFrom: Allows contracts to transfer tokens on behalf of the owner.
• approve: Allows one address, the owner, to grant permission to another address, a delegate, to spend a certain number of tokens on its behalf.
• allowance: Returns how many tokens the delegate is allowed to use on behalf of the owner.
Optional features: token name, character, and number of possible decimal places.**The importance of ERC-20 to the Ethereum Ecosystem**The ERC-20 standard provides a meaningful premise for interoperability within the Ethereum ecosystem in that it engenders the ability of tokens to work with other smart contracts. This, in turn, makes the integration of any new tokens into an already working application or service more facile: wallets, exchange platforms, and DeFi. - Management tokens: entitle the holder to vote on the management of a project or a platform concern in question.
- Security tokens: a class of tokens that give a right to some sort of dividend distribution or income derived from some project.
- Stablecoins: a class of cryptocurrencies that are pegged to a certain fiat currency or some other underlying asset, with the immediate implication of this being stability in their price.
- Challenges and LimitationsDespite the popularity of the ERC-20 standard, there are a few shortcomings in the standard design itself, such as the lack of a standardized way of preventing the accidental sending of tokens to contracts that cannot process them. There have been new standards developed, such as ERC-223 and ERC-721 for non-interchangeable tokens, that try to bridge some of these shortcomings.
ERC-20 still is one of the most meaningful and influential standards on the Ethereum blockchain. It has underpinned an uncountable number of projects and tokens, building up a contribution to the further development and growth of both decentralised finance and applications. Although limited, ERC-20 is still one of the most popular and versatile standards in the cryptocurrency world.
What is TRC-20?
TRC-20 is a token standard within the TRON blockchain for creating and deploying DApps and smart contracts on the TRON ecosystem. Like ERC-20 in Ethereum, it describes the rules that tokens should abide by in order to coexist in the TRON blockchain. This standard ensures the same interoperability between all different decentralized applications, games, exchanges, wallets, and other services.
Features and Benefits of the TRC-20
- High Performance: TRON is designed for high performance and high scalability; hence, TRC-20 tokens are suitable for mainstream application in applications requiring fast transactions.
- Ethereum Compatibility: Because of the similarity to ERC-20, it is easy for developers to move their projects from Ethereum to TRON, which accelerates both the growth and diversity of the TRON ecosystem.
- Low Transaction Costs: Due to low transaction costs, one of the key advantages of the TRC-20 is that it makes the usage of tokens economically feasible both for the end user and the developer.
Technical Details
The TRC-20 standard defines functions and events similar to ERC-20, including:
- TotalSupply: Returns the total number of tokens in circulation.
- BalanceOf: Displays the balance of tokens at an address in question.
- Transfer: Allows tokens to be transferred between addresses.
TransferFrom, approve, and allowance: These will enable the management of tokens on behalf of other addresses; thus, it will enable advanced financial mechanisms such as automated management or even decentralized exchanges.
Application of TRC-20
TRC-20 tokens have multiple use cases and applications on the TRON ecosystem, including but not limited to:
- DeFi: Stablecoin creation, creation of control tokens, and other kinds of financial instruments.
- DApps: Tokens have the potential to be used as an internal currency for games, social networks, and so on.
- Digital Assets and Collectibles: While TRC-20 tokens are not typically used to represent NFTs, another standard called TRC-721 is generally followed, but they could still be in related ecosystems for trading and exchanging digital assets.
Similar to other blockchain networks, TRON and the TRC-20 standard face their own challenges. Scalability, security, and decentralization are still an issue for such digital assets. As long as the technology continues to evolve and more developers get involved with users, the place of TRON is secure among the big platforms of decentralized applications and financial services creation and usage.
TRC-20 is a keystone within the TRON ecosystem because it provides a uniform and functional way of creating tokens for everything—from simple tokens to complex protocols that solve different problems. Performance, coupled with low transaction fees and interoperability with other standards, puts TRC-20 in the front line of blockchain and decentralized technologies development.
What is cryptocurrency mining?
Mining cryptocurrency is the process of verifying transactions and adding them onto a public ledger that everybody is supposed to have a copy of; this public ledger is what is referred to as the blockchain. It also entails the issuance of new coins into the supply circulation as an incentivization for work done. Mining is part and parcel in many digital cryptocurrencies’ security and operations, including Bitcoin and Ethereum before its transition to Proof of Stake. And many others.
How Mining Works
- Consensus algorithms are the basis of mining. Any given consensus algorithm defines how the participants of the network achieve a common view on the current state of the blockchain. The most popular ones are Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, though mining is directly related mainly to PoW.
- Proof of Work: Miners in the PoW network are competing to solve complex mathematical puzzles, which require huge computational resources. The first miner coming up with a solution wins the right to add another block to the chain and receives cryptocurrency as a reward.
- Mining difficulty: This automatically readjusts itself via the sum of all network processing power to ensure that the average time in finding a new block is kept at a constant level.
- Mining equipment
- ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit): Chips specifically designed to mine a particular cryptocurrency. They have the best performance for mining but are very expensive to purchase and highly over-specialized for general usage.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): Though video cards capable of mining a range of cryptocurrencies are less effective than the ASICs, they are much more versatile.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): Mining based on processors is practically not used now because of its low efficiency and too high competition from ASICs and GPU.
Environmental impact
Mining—especially PoW-based mining—is very power-consuming, and its impact on the environment has become a matter of great concern. Finding alternative consensus algorithms that require less energy and adopting renewable sources of energy will increasingly become critical to making cryptocurrencies greener.
The future of mining
As everything would point out, in the presence of the environmental, technical, and economic challenges of the future of cryptocurrency mining, there would probably be a change over to more sustainable forms of mining and blockchain network maintenance. There is already a trend that moves away from PoW to PoS and other alternative algorithms that require less energy.
Whereas mining is essential to the functioning and security of a blockchain network, recently it has been under much scrutiny due to its environmental footprint. Indeed, the quest for balance between security, efficiency, and sustainability within the cryptocurrency ecosystem is among the main open challenges.
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving is an event occurring when the reward for mining a new block on the bitcoin blockchain is reduced by half. This mechanism was installed in the bitcoin protocol by its creator—or group of creators—under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Each four years or so, exactly every 210,000 blocks, halving takes place. This is how inflation is kept in check and fewer new coins enter the market until all 21 million bitcoins have been reached.
How the halving works
Frecuencia: Every 4 years, approximately. It happened for the first time in 2012, then in 2016, and finally in 2020.
Mechanism: At the moment of halving, at that instant, the reward given to miners when they find a block is reduced by half. Example: If before the halving, miners were using 12.5 bitcoins per block, after the halving, they will only take 6.25.
Inflation: Halving controls the inflation in the bitcoin ecosystem by slowly reducing the speed at which coin supply increases.
Bitcoin Price: So far, with each halving, interest in bitcoin has grown along with its price. This is all out of anticipation of a decreased supply of new coins coming into the market.
Mining: For miners, halving means a decrease in bitcoin revenue per block found. This can lead to less efficient miners going out of business and an increase in the concentration of hashrate in the hands of big players.
Prospects after the 21 million limit is reached
- Transaction fees: Once the last bitcoin is mined, transaction fees would completely dominate miners’ revenue. This alone should be a good-enough incentivization for miners to keep the network going.
- Price impact: With the demand growing, if the supply of bitcoins is kept in check, it can become a driver of its value in the long run.
A halving is a critical event that happens in the life of Bitcoin, influencing everything from inflation to the dynamics of price action within the ecosystem. It underlines how precisely opposite in nature bitcoin is, being deflationary in contrast to the inflationary monetary policy of traditional fiat currencies. While the short-term implications are very far from certain, long-term effects of a halving tend to be unquestionably considered positive for the value and attractiveness of bitcoin as an asset for investment.
What is a Cold Wallet?
Among the means of cryptocurrency storage, the security of funds is the biggest concern for any investor and user in general. A cold wallet is a means of storing cryptocurrency that offers very strong security since it does not have a continuous internet connection. On the other hand, hot wallets provide ease in terms of speed in transactions, along with high risk in terms of hacking attacks. In this article, we look at what a cold wallet is, its pros and cons, and what varieties of cold wallets are available.
What is Cold Wallet?
A cold wallet is basically a hardware or physical storage device, disconnected from the internet, used in storing cryptocurrency assets. It is mainly employed for purposes of ensuring safety against online attacks and unauthorized access to one’s funds. Cold wallets can be in the form of USB devices, paper wallets, or even special hardware devices.
Advantages of Cold Wallets
- Security: There is minimal risk of cyber attack and hacking because of the system being always offline rather than on the internet 24/7.
- Control: The user has full control over their cryptocurrency assets since the keys are kept offline, thus in control and possession of the owner.
- Virus Resistant: Since the data isn’t transferred over the internet, cold wallets are not prone to any virus or malware attacks in the software.
- Usability: The transaction requires moving funds from a cold wallet to a hot wallet, which is not as convenient as having all the hot wallets constantly at your disposal.
- Risk of loss: If there is loss or damage to a physical device, it could be very hard or even impossible to recover access to funds.
- Start-up costs: Some hardware cold wallets are quite costly to buy.
Types of Cold Wallets
Hardware Wallets: Special flash drive-like devices allow them to store keys of cryptocurrency offline and conduct transactions by connecting to a computer that needs them.
Paper Wallets: A physical document carrying public and private keys on paper in the form of a QR code or others. It is viewed as one of the most secure wallets because information on it cannot be stolen online.
Metal Wallet: A device for storing key information in metal plates; these are resistant against physical wear and tear as well as against water and fire.
Cold wallets are one of the most important tools in securing cryptocurrency assets. When choosing among hardware, paper, and metal wallets, the users need to weigh their needs for security, convenience, and cost. Though there are some disadvantages in use and risks associated with the loss of the hosting device, the benefits of cold storage outweigh them, and it is preferable for the long-term preservation of significant cryptocurrency means.
How much bitcoin can you mine?
The quantity of bitcoin that can be mined is, by the Bitcoin algorithm and by design, strictly limited to a maximum of 21 million no more. Satoshi Nakamoto set this limit and considered it an integral part of Bitcoin monetary policy in order to avoid inflationary pressures. As that limit is approached, the reward for mining new blocks is reduced by about half roughly every four years through a process called the halving. The last bitcoin will likely be mined around 2140, at which time the miners will only be rewarded via transaction fees for processing transactions and maintaining the blockchain.
How many are mined currently?
Up until the beginning of 2024, about 19,361,400 bitcoins have been mined, considering a halving every four years and the original block reward was of 50 Bitcoins, which diminishes with each halving.
Where can I buy cryptocurrency safely?
Buying cryptocurrency has become mainstream, but it is always important to go through the process with due care for your investment’s safety. Here goes a shortlist of what one should pay attention to when choosing a platform for buying cryptocurrency:
| Criteria | Details |
|---|---|
| Platform reputation | Choose exchanges and platforms with a good reputation, longevity in the market, and positive user feedback. Research should be conducted online, through forums, and specialized websites. |
| Security features | Ensure that the chosen site has implemented advanced security features, including but not limited to 2FA, holding most funds in cold wallets (not connected to the internet), and other data protection protocols. |
| Regulation | Prefer regulated platforms, especially those in jurisdictions with clear cryptocurrency rules, as they provide an additional layer of protection and reliability. |
| Commissions and fees | Consider the fee structure on the platform. Fees can vary widely and include transaction fees, withdrawal fees, and currency exchange fees. |
| Ease of use | The platform should be transparent, user-friendly, and feature a simple registration system with subsequent verification; it needs to be intuitive. |
Examples of well-known and reliable platforms:
Coinbase: One of the largest, most famous crypto exchanges worldwide, offers a wide variety of cryptocurrencies for purchase or sale.
Binance: The world’s biggest cryptocurrency exchange in terms of trading volume, including hundreds of types of cryptocurrencies and financial services on offer.
Kraken: Has gained a reputation because of its high level of security and numerous types of cryptocurrencies available.
Bitstamp: Founded in 2011, Bitstamp is one of the earliest cryptocurrency exchanges. It boasts excellent reliability and ease of use.
But before that, it’s good to do your research and compare the conditions and security between different platforms. And, of course, always keep in mind that there are high risks involved, including losing the investment you made with cryptocurrencies.
Where and how can you buy cryptocurrency?
With the different online platforms and services, buying cryptocurrency has become more affordable and relatively easy. Here is a step-by-step guide on how you can buy cryptocurrency:
| Step | Details |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Choosing a Cryptocurrency Exchange or Broker | First, choose a platform to buy cryptocurrency. This may be a cryptocurrency exchange (e.g., Binance, Coinbase, Kraken) or a broker. Select a reliable and secure platform with a good reputation. |
| Step 2: Account Registration and Verification | After selecting the platform, create your account. The process typically starts with email verification and a request for personal details. Many platforms require you to go through a KYC process, uploading a photo ID and verifying your residential address. |
| Step 3: Deposit funds | To buy cryptocurrency, deposit fiat money—usually USD or EUR—into your exchange or broker account. You can do this via bank transfer, debit or credit cards, or other available payment systems. |
| Step 4: Buying cryptocurrency | With your balance funded, you can make a cryptocurrency purchase. Choose the cryptocurrency you want to buy and specify either the amount in fiat currency or the quantity of cryptocurrency. Confirm the transaction as instructed on the platform. |
| Step 5: Cryptocurrency Storage | Store your cryptocurrency on the exchange after purchase or send it to your cold wallet for more security. There are hot wallets (online) and cold wallets (offline) for storage. |
Important considerations:
Security: Two-factor authentication; protection of personal information and means.
Commissions: Consider all transaction fees and exchange rates, as these may be very different from platform to platform.
Taxes: Keep in mind whether your country taxes received incomes from trading cryptocurrencies and pay your contributions on time.
Risks: The cryptocurrency market is very volatile, and investing in cryptocurrencies includes a high level of risk of losing your investment.
This will allow you to safely and efficiently buy cryptocurrency on a platform of your choice.
What is Bitcoin ATM?
A Bitcoin ATM is such a real-world, physical terminal that lets users buy or sell bitcoin for cash; sometimes, this would be achieved by using bank cards directly. Such devices make the interaction with cryptocurrencies much easier for the wider audience by offering a convenient and quick method of performing transactions without needing to go through the tedious process of signing up with cryptocurrency exchanges.
The Key Features of Bitcoin ATM:
Accessibility: BTC ATMs are spread across public points, like shopping centers, airports, cafes, and so on. Because of this, buying and selling cryptocurrencies becomes very comfortable for the wide audience.
Anonymity: Although some ATMs request one identification verification processes, where one gets scanned for his or her identity card or entered via a phone number, most of them have the possibility of going anonymous, especially in small purchases.
High commissions: Fees associated with exchanging via Bitcoin ATMs are highly expensive compared to commissions of virtual cryptocurrency exchanges. The commissions vary and may get as high as 5-10% or even more of the transaction amount.
The procedure goes like this:
Purchasing cryptocurrency: If one wants to buy bitcoin, then he has to deposit cash in the ATM, scan the QR code of his bitcoin wallet with his mobile device, and the kiosk transfers the purchased amount to the wallet.
Selling cryptocurrency: In order to sell bitcoin, a user selects the amount he wants to sell and provides the QR code of his wallet in which he will get the funds. The confirmation with bitcoins prompts the ATM to spit out money in cash.
Using a Bitcoin ATM is super convenient with regard to access to cryptocurrencies, especially for people who do not feel comfortable disclosing too much personal information in deals or when someone is in a hurry and has to buy or sell small portions of cryptocurrency. On the other hand, this usage involves paying high commissions and possible identity disclosure.
Also, it is worth mentioning that in this case, lawyers from Regulated United Europe provide legal services regarding obtaining a crypto license.
Bitcoin history
Bitcoin, the world’s first and most famous cryptocurrency, appeared in 2009 and radically changed the idea of money and financial transactions. This decentralised digital currency offered a new model of economic independence that did not require the involvement of traditional banking and government structures. In this article, we will look at the history of Bitcoin, from its creation to its impact on modern financial systems.
Establishment and early years
Bitcoin was created by a person (or group of people) under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. On 31 October 2008, Nakamoto published the article “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, which described the concept of a cryptocurrency powered by blockchain technology. On 3 January 2009, the first block, known as the genesis block, was mined and the history of Bitcoin began.
Main stages of development
- 2010: The first transaction was made when programmer Lazlo Hanech paid 10,000 bitcoins for two pizzas. This event is still celebrated in the crypto community as “Bitcoin Pizza Day”.
- 2013: Bitcoin reaches the $1,000 level, but its value soon plummets due to hacking attacks and regulatory issues.
- 2017: Bitcoin reaches new heights, surpassing the $20,000 per coin mark, attracting widespread attention from investors and media alike.
- 2020-2021: A period of significant growth when Bitcoin surpasses $60,000 for the first time, driven in part by economic instability related to the COVID-19 pandemic and increased institutional investment.
Technological impact
Blockchain technology, the underlying technology behind Bitcoin, has had a significant impact on a multitude of industries, offering ways to improve transparency, security and efficiency. Blockchain has found applications in areas such as logistics, healthcare, law and more.
Impact on the global financial system
Bitcoin has generated significant interest from regulators around the world and fuelled debate about the future of money. Some countries have accepted cryptocurrency as a legal tender, while others have imposed strict restrictions or bans. This highlights the growing recognition of cryptocurrencies as a significant factor in the global economy.
The story of Bitcoin is an amazing testament to a revolution in the world of finance that continues to evolve today. From an anonymous publication on the internet to a worldwide phenomenon, Bitcoin has travelled a path that has changed not only how we think about money, but also how we can use technology to create a more open and accessible financial system. The future of this cryptocurrency and the ongoing innovation around it remains the subject of lively debate and huge interest.
Solana history
 Solana is one of the fastest growing blockchain platforms on the cryptocurrency market, which has managed to attract significant attention from both investors and developers in a short period of time. The main goal of Solana is to create a high-performance, secure and scalable blockchain system that could process thousands of transactions per second with minimal cost. In this article, we will take a detailed look at the history of Solana’s development, the main stages of its formation and the innovative solutions offered by the platform.
Solana is one of the fastest growing blockchain platforms on the cryptocurrency market, which has managed to attract significant attention from both investors and developers in a short period of time. The main goal of Solana is to create a high-performance, secure and scalable blockchain system that could process thousands of transactions per second with minimal cost. In this article, we will take a detailed look at the history of Solana’s development, the main stages of its formation and the innovative solutions offered by the platform.
Founding and development
Solana was founded in 2017 by Anatoly Yakovenko, who previously worked as an engineer at Qualcomm and Dropbox. The idea of creating a new blockchain platform came to Yakovenko after he encountered scalability issues and high fees that were typical of then-existing blockchains, including Bitcoin and Ethereum.
A key innovation offered by Solana was Proof of History (PoH) technology, a method for creating a historical record of time that increases the speed and scalability of the blockchain. This technology allows nodes in the network to create their own “time stamps” on blocks without having to wait for confirmation from other nodes.
Early development and testing
Initial testing of the Solana network began in 2018, with the first alpha version of the network launching in February 2020. These early tests showed that PoH technology could process thousands of transactions per second, which far exceeded the performance of most other blockchain systems.
Official launch and growth
The official launch of the Solana core network took place in March 2020. Since then, the platform has been rapidly gaining popularity, especially in the areas of decentralised finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFT), where high transaction speeds and low fees are critical.
By 2021, Solana has solidified its position as one of the leading platforms for developing and running decentralised applications, thanks to which the value of its SOL token has grown tenfold. Investors and developers value Solana for its innovative approach to solving scalability and performance problems.
Current situation and outlook
At the moment, Solana continues to grow, attracting more projects and partnerships. The platform is actively working on improving its technology, including improvements in network security and stability. Due to its potential and active community support, Solana is considered one of the most promising blockchain platforms on the market.
Solana’s story demonstrates how innovative technology can change the cryptocurrency landscape and open up new opportunities for users and developers. It can be used to not only speed up transactions, but also reduce the cost of interactions on the blockchain, making the technology accessible to a wide range of applications. Given current trends, the future of Solana looks promising, with great opportunities for further growth and innovation.
Tether USDT history
 Tether (USDT) holds a unique place in the cryptocurrency world as one of the first and most widely used stablecoins. Founded in 2014, Tether was designed to combine the best of both worlds: the stability of traditional fiat currencies and the flexibility of cryptocurrencies. This stablecoin is pegged to the value of fiat currencies such as the US dollar, euro and Japanese yen, providing stability and reducing the risk of volatility. In this article, we will look at the history of Tether, its impact on the cryptocurrency market and the challenges it has faced throughout its existence.
Tether (USDT) holds a unique place in the cryptocurrency world as one of the first and most widely used stablecoins. Founded in 2014, Tether was designed to combine the best of both worlds: the stability of traditional fiat currencies and the flexibility of cryptocurrencies. This stablecoin is pegged to the value of fiat currencies such as the US dollar, euro and Japanese yen, providing stability and reducing the risk of volatility. In this article, we will look at the history of Tether, its impact on the cryptocurrency market and the challenges it has faced throughout its existence.
Founding and Early Years
Tether was launched in October 2014 by Tether Limited, part of Bitfinex, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges. Tether’s goal was to create a “stable” cryptocurrency equivalent to the US dollar that could be used on blockchain networks and be a bridge between fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies. Each USDT was to be backed by a dollar in a bank account, which theoretically ensured its stability.
Growth and Popularity
Tether’s popularity began to grow along with the expansion of the cryptocurrency market. USDT quickly became the preferred vehicle for traders to hedge volatility risk, make inter-exchange transfers and manage liquidity without having to exit into fiat currencies, which often involves high fees and regulatory delays.
Problems and Criticism
As Tether grew in popularity, questions began to arise regarding its collateral. Critics and regulators expressed concerns about the transparency and reliability of Tether’s reserve information. This was especially true whether all USDT coins were indeed fully backed by real dollars. These concerns have led to several forensic probes and investigations by regulators.
Regulatory Challenges and Solutions
Tether Limited faced a number of regulatory challenges, including a lawsuit from the New York Attorney General, which was settled in February 2021. As part of the settlement, the company agreed to provide regular reports on its reserves and improve the transparency of its operations.
Current Situation and Future
Despite the challenges, Tether remains one of the most widely used stablecoins in the industry. It plays a key role in providing liquidity on cryptocurrency exchanges and is used in various blockchain projects. Tether’s prospects are closely linked to the overall development of the cryptocurrency market and the company’s ability to adapt to changing regulatory requirements.
The story of Tether demonstrates both the opportunities and risks associated with innovation in digital currencies. Its evolution from a simple stablecoin to an important financial instrument emphasises the need to balance innovation with regulatory clarity. Going forward, Tether’s success will depend on its ability to maintain user trust and meet financial standards while providing stability and security for a wide range of transactions in the cryptocurrency world.
USDC history
 USD Coin (USDC) is a stablecoin that was created to combine the benefits of blockchain technology with the stability of traditional currency, in this case the U.S. dollar. USDC is a digital version of the USD, with each unit backed by a real dollar or equivalent assets held in bank accounts. In this article, we will look at the history of USDC, the main stages of its development and its role in the modern cryptocurrency ecosystem.
USD Coin (USDC) is a stablecoin that was created to combine the benefits of blockchain technology with the stability of traditional currency, in this case the U.S. dollar. USDC is a digital version of the USD, with each unit backed by a real dollar or equivalent assets held in bank accounts. In this article, we will look at the history of USDC, the main stages of its development and its role in the modern cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Establishment and goals of the USDC
USD Coin was launched in September 2018 by Circle and Coinbase as part of the CENTRE consortium initiative. The main goal of creating USDC was to offer the market a stablecoin that combines the reliability of traditional finance with the innovative capabilities of cryptocurrencies. This stablecoin is designed for a wide range of applications, including trading on cryptocurrency exchanges, fund transfers, salary payments and use in decentralised finance (DeFi).
Development and regulatory adaptation
USDC has quickly gained popularity due to its strict adherence to regulatory standards and transparency in currency collateralisation. Each USDC dollar is backed by a U.S. dollar held in accounts that are subject to regular audits by independent audit firms. This transparency has ensured investor and user confidence, which has been one of the key drivers of USDC’s growth and acceptance.
Integration with financial systems
One of the significant achievements of USDC has been its widespread adoption not only in cryptocurrency projects, but also in more traditional financial systems. For example, in 2021 Visa began accepting USDC transactions through its payment network, a significant step towards integrating cryptocurrencies into everyday financial transactions.
Growth and current status
USDC has seen impressive growth in its short lifespan. As of 2021, the total amount of USDC in circulation has increased significantly, reflecting the growing confidence in this cryptocurrency and its stability in the market. USDC is not only used as a medium of exchange, but also as an important tool in the DeFi ecosystem, providing stability and liquidity across various financial protocols.
USD Coin (USDC) has had a significant impact on the cryptocurrency market, becoming one of the most stable and trusted stablecoins. With strict regulatory standards, transparency, and widespread acceptance in the financial world, USDC continues to play a key role in the further development of cryptocurrencies and their integration into the global economy. In the future, USDC has the potential to become one of the leading bridges between traditional and digital finance, continuing to push the boundaries of opportunity for users and businesses around the world.
Etherium history
 Ethereum is undoubtedly one of the most significant technological innovations in today’s digital world. Since its inception in 2015, Ethereum has offered the concept of smart contracts, radically expanding the possibilities of using blockchain technology. This platform has not only facilitated the development of cryptocurrencies, but also laid the foundation for decentralised applications (DApps), which are now making their way into a wide variety of sectors. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the history of Ethereum’s development, its major milestones and its impact on the digital economy.
Ethereum is undoubtedly one of the most significant technological innovations in today’s digital world. Since its inception in 2015, Ethereum has offered the concept of smart contracts, radically expanding the possibilities of using blockchain technology. This platform has not only facilitated the development of cryptocurrencies, but also laid the foundation for decentralised applications (DApps), which are now making their way into a wide variety of sectors. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the history of Ethereum’s development, its major milestones and its impact on the digital economy.
Ethereum’s foundation
Ethereum was proposed in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, then a 19-year-old programmer and co-founder of Bitcoin Magazine. Vitalik was convinced that blockchain technology could be used not only to create cryptocurrencies, but also to execute software code, allowing developers to create complex decentralised applications. This idea was received with enthusiasm, and in January 2014, the Ethereum project was officially announced at the North American Bitcoin Conference in Miami.
Development and key milestones
- Pre-sale of tokens (2014): To fund development, Ethereum ran one of the most successful fundraising campaigns in cryptocurrency history, raising about $18 million.
- Network Launch (2015): The Ethereum blockchain was launched on 30 July 2015. This launch ushered in the era of smart contracts, which automate the fulfilment of contractual obligations using blockchain technology.
- DAO and network partitioning (2016): In 2016, the Decentralised Autonomous Organisation (DAO) project faced a serious threat in the form of a hacker attack that resulted in a significant amount of funds being stolen. This incident led to significant debate in the community and the subsequent split of the blockchain into two separate chains, Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC).
- Transition to Proof of Stake (2020 – 2022): Ethereum has begun the transition from the Proof of Work consensus mechanism to the more efficient and environmentally sustainable Proof of Stake. This process, known as Ethereum 2.0, aims to improve the scalability, security and sustainability of the platform.
Impact on the industry
Ethereum has had a huge impact on the development of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies. Ethereum smart contracts have enabled developers to create a wide range of applications, from financial and insurance services to games and social networks. Ethereum has also played a key role in popularising the concepts of ICO (Initial Coin Offering) and DeFi (decentralised finance), which have revolutionised the way capital is raised and financial services are provided without intermediaries.
The story of Ethereum is a vivid example of how an innovative idea can turn into a global technological movement that can change many industries. Today, Ethereum continues to evolve, adapting to new challenges and opportunities. The transition to Ethereum 2.0 and further improvements in smart contract technology herald new prospects for broadening and deepening its impact on the digital economy.
BNB history

Binance Coin (BNB) is a cryptocurrency created by cryptocurrency exchange Binance, one of the largest and most popular exchanges in the world. Since its launch in 2017, BNB has undergone significant changes and expansion in its functions, becoming not only a means to reduce exchange fees, but also an important element of the wider Binance ecosystem. In this article, we take a look at the history of BNB, its growth, transformation and current importance to the cryptocurrency community.
Background and initial objectives
Binance Coin was launched in July 2017 through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO), which helped the Binance exchange raise the necessary capital for further development. BNB was originally created on the Ethereum blockchain as an ERC-20 standard token. The main function of the token was to provide discounts on fees for exchange users, which made it an attractive investment and trading asset.
Transition to a proprietary blockchain
In April 2019, BNB migrated from the Ethereum blockchain to its own Binance Chain blockchain. The move was aimed at improving the performance and scalability of transactions using BNB, and also gave Binance the ability to run decentralised applications (DApps) and other cryptocurrency projects on its platform.
Increased utilisation
Over time, the use of BNB has expanded significantly. In addition to the function of reducing commissions on the exchange, BNB was used to participate in tokensales on the Binance Launchpad platform, as well as a means of payment in various services, including payment for trading operations, purchase of goods and services from Binance partners, and even as a means of payment in charitable projects through Binance Charity.
Decentralisation and innovation
In addition to functional expansion, BNB plays a key role in supporting innovation on the Binance network. This includes support for decentralised finance (DeFi) on the Binance Smart Chain, an Ethereum-compatible blockchain that allows developers to build Ethereum-compatible applications with lower transaction fees and higher performance.
Current situation and outlook
BNB is currently one of the largest cryptocurrencies by market capitalisation and remains an important part of the Binance ecosystem. BNB’s success is linked to Binance’s growth as a platform for cryptocurrency trading and a centre of blockchain innovation. BNB’s prospects are closely linked to the future of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, and it is expected to continue to play an important role in the development of this rapidly changing industry.
The story of Binance Coin reflects the dynamic development of the cryptocurrency market and the ability of cryptocurrencies to adapt and evolve in response to changing needs and technological trends. BNB has not only solidified its position as one of the leading cryptocurrencies, but also continues to support innovation that can lead to greater adoption of cryptocurrencies on a global scale.
XRP history
 XRP, often referred to in the context of the related company Ripple, is one of the most talked about cryptocurrencies in the industry. Designed to revolutionise international payments and bank transfers, XRP offers fast, secure and cheap cross-border payments. In this article, we take a look at the history of XRP, from its creation to its current market position, as well as its impact on international payment systems.
XRP, often referred to in the context of the related company Ripple, is one of the most talked about cryptocurrencies in the industry. Designed to revolutionise international payments and bank transfers, XRP offers fast, secure and cheap cross-border payments. In this article, we take a look at the history of XRP, from its creation to its current market position, as well as its impact on international payment systems.
Origins and objectives
XRP was created in 2012 by three engineers – Jed McCaleb, Chris Larsen and Arthur Britto. The main goal of XRP is to improve international payments, which have traditionally suffered from high fees and long processing delays. The technology behind XRP is designed to operate at maximum efficiency and minimum cost, making it ideal for the global financial sector.
Early development and implementation
XRP has quickly caught the attention of major financial institutions due to its unique characteristics. Unlike many other cryptocurrencies, XRP does not require mining, making it more environmentally friendly and less resource-intensive. Instead, all 100 billion XRP coins were “pre-mined” and distributed to the creators and Ripple Labs.
Growth and partnerships
Ripple, the company behind XRP, has been actively working with banks and payment processors to integrate its technology. This has included the launch of its xRapid product, which uses XRP as a bridge currency to enable faster and cheaper transaction processing. Ripple’s partners include major players such as Santander, PNC Bank and American Express, which has greatly increased confidence in XRP in the financial world.
Issues and challenges
Not everything has been smooth sailing in the XRP story. Ripple Labs has faced criticism and legal action, including allegations that XRP was sold as an unregistered security. These legal challenges caused significant fluctuations in the price of XRP and affected its perception in the investment community.
Current situation and future
Despite legal challenges, XRP remains one of the leading cryptocurrencies in terms of market capitalisation. Its support from major banks and financial institutions continues to be strong, demonstrating XRP’s potential as an important player in the world of digital finance. The future of XRP will depend on the outcome of the litigation and its ability to adapt to the changing regulatory and technological environment.
The XRP story is an example of how innovative technology can cause significant change in established industries such as banking payments. XRP has demonstrated the potential of blockchain beyond a mere medium of exchange, offering solutions to real-world problems in finance. Its development and impact will continue to be a focus for market participants and regulators alike.
Litecoin history
 Litecoin (LTC) is one of the oldest cryptocurrencies, often described as the “silver to Bitcoin’s gold”. Since its inception in 2011, Litecoin has become one of the most recognisable and widely used altcoins on the market. This cryptocurrency was designed to provide fast, secure and affordable payments through the use of blockchain technology. In this article, we will look at the history of Litecoin, its development and its contribution to the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Litecoin (LTC) is one of the oldest cryptocurrencies, often described as the “silver to Bitcoin’s gold”. Since its inception in 2011, Litecoin has become one of the most recognisable and widely used altcoins on the market. This cryptocurrency was designed to provide fast, secure and affordable payments through the use of blockchain technology. In this article, we will look at the history of Litecoin, its development and its contribution to the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Founding and development
Litecoin was created by Charlie Lee, a former Google employee who saw potential in Bitcoin’s technology but sought to improve it. Lee began work on Litecoin in 2011, and the network was launched on 13 October that year. Litecoin is a fork of Bitcoin, but it has been modified to provide a shorter block creation time of 2.5 minutes versus Bitcoin’s 10 minutes, allowing for faster transactions.
Technical improvements
Litecoin used the Scrypt hashing algorithm instead of the SHA-256 algorithm used in Bitcoin. This was done to make Litecoin less accessible to ASIC miners and more accessible to users with regular computers. However, over time, ASIC miners have also come to dominate Litecoin mining.
Growth and popularity
Litecoin quickly gained popularity due to its improvements over Bitcoin and became one of the major altcoins on the market. The key success factors were its speed, efficiency, and wide availability on multiple cryptocurrency exchanges. Litecoin was also actively used as a testbed for innovations that could later be adapted for Bitcoin, such as Segregated Witness (SegWit) and the Lightning Network.
Projects and innovations
In addition to technical improvements, Litecoin has been actively experimenting with new technologies. For example, in 2017, Litecoin became one of the first major cryptocurrencies to successfully integrate and test SegWit technology, which improved the scalability of the network.
Current situation and outlook
Despite its market resilience, Litecoin continues to face competition from new cryptocurrencies and blockchain projects. However, its active community and constant pursuit of innovation keep it relevant in the rapidly changing world of cryptocurrencies. Litecoin continues to be valued for its stability, speed and low transaction costs, making it an attractive choice for both new and experienced cryptocurrency users.
The story of Litecoin is a tale of constant adaptation and improvement in response to changing technological and market conditions. Relatively minor changes to Bitcoin’s code led to the creation of a new cryptocurrency that was able to gain a steady place in the ranking of leading cryptocurrencies. Litecoin’s continued development and its contribution to blockchain innovation leave it an important and valuable asset in the crypto market.
Dogecoin history
 Dogecoin (DOGE) started as a joke project, but quickly turned into one of the most popular cryptocurrencies in the world. Launched in December 2013, this unusual project was originally created to parody numerous altcoins. However, thanks to its friendly community and unconventional approach to marketing, Dogecoin has gained widespread popularity and serious support. In this article, we take a look at the history of Dogecoin, from its inception to its status as an iconic cryptocurrency.
Dogecoin (DOGE) started as a joke project, but quickly turned into one of the most popular cryptocurrencies in the world. Launched in December 2013, this unusual project was originally created to parody numerous altcoins. However, thanks to its friendly community and unconventional approach to marketing, Dogecoin has gained widespread popularity and serious support. In this article, we take a look at the history of Dogecoin, from its inception to its status as an iconic cryptocurrency.
Inception of an idea
Dogecoin was created by programmers Billy Marcus from Portland, Oregon, and Jackson Palmer, who worked in Sydney, Australia. Palmer got the idea for the currency when he laughed at the growing number of altcoins and decided to create his own, based on a popular internet meme at the time involving a Shiba Inu dog. Marcus, who was already working on his own cryptocurrency project, was inspired by the idea and helped turn the joke into a reality.
Rapid growth and development
After launching, Dogecoin quickly gained popularity due to its humorous approach and active community. The currency has become popular among internet users as a means of tipping for interesting content on platforms such as Reddit and Twitter. Dogecoin has also established itself as a charitable currency, raising money for various social and sporting projects, including funding the Jamaican bobsleigh team’s participation in the 2014 Winter Olympics.
Cultural and media influence
Dogecoin is different from other cryptocurrencies because of its unique culture that values humour and informal communication. This characteristic has helped it gain popularity among a wide audience and made it an important part of online culture. Dogecoin’s frequent mentions on social media and its popularity among celebrities, including Ilon Musk, have greatly enhanced its media presence and helped it grow in value.
Market fluctuations
Like many other cryptocurrencies, Dogecoin is subject to significant market fluctuations. Despite its unserious roots, it has reached significant heights in market capitalisation, especially during periods of intense interest in cryptocurrencies. These fluctuations are often caused by changes in general market sentiment and speculative trading.
The story of Dogecoin demonstrates how an initially humorous project can turn into a powerful financial instrument with a strong community and broad influence. Dogecoin epitomises a unique combination of technological innovation and cultural phenomenon, continuing to be one of the most interesting phenomena in the world of cryptocurrencies.
Troncoin history

Tron (TRX) is one of the leading blockchain platforms designed to decentralise internet content and change the way content creators and their audiences interact. Launched in 2017 by Justin Sun, the Tron platform aims to improve revenue distribution on the internet by providing tools to build free, global and decentralised applications. In this article, we take a look at the history of Tron, its key milestones and its current state in the market.
Foundation and mission
Tron was founded by Justin Sun, who previously worked as Ripple’s China representative and founded Peiwo, one of the largest voice messaging apps in China. The idea for Tron grew out of a desire to create a fully decentralised platform that would allow content creators to interact directly with consumers, bypassing intermediaries such as Google Play and the Apple App Store, and thereby increase their revenues.
Early development and ICOs
Tron was initially presented as an Ethereum-based project with an ERC-20 token. In September 2017, the company held an initial coin offering (ICO), which became one of the most successful at that time, raising $70 million. These funds were used to further develop the platform and expand its functionality.
Transition to a proprietary blockchain
In June 2018, Tron officially switched from Ethereum to its own blockchain. The move was aimed at improving scalability, transaction speed, and project independence. The proprietary blockchain allowed Tron to create decentralised applications (DApps) and conduct transactions faster and more efficiently than was possible on the Ethereum platform.
Ecosystem development and acquisitions
Tron has been actively developing its ecosystem, including the launch of its own cryptocurrency wallet, blockchain games and social media applications. In 2018, Tron acquired BitTorrent, a popular file-sharing service, which allowed it to integrate blockchain technology into its file distribution system and strengthen its market presence.
Current situation and future
Tron is currently one of the leading platforms for developing DApps, constantly competing with other major players such as Ethereum and EOS. With its high performance, scalability and active community, Tron continues to attract developers and investors. The platform is constantly being updated and developed, striving to become a leader in decentralised internet technologies.
Tron’s story is an example of how a fledgling startup can grow into a large and influential blockchain platform. Tron’s focus on decentralising content and commitment to innovation has allowed it to carve out a unique niche in the market. In the future, Tron is likely to continue to play a significant role in the digital economy, offering new opportunities for content creators and consumers around the world.
Cardano history
 Cardano is a blockchain platform that has established itself as one of the most innovative in the cryptocurrency industry. Developed with a focus on a scientific approach and high security standards, Cardano is an advanced platform for creating decentralised applications and smart contracts. In this article, we will look at the history of Cardano’s development, the key stages of its formation and its current position in the cryptoecosystem.
Cardano is a blockchain platform that has established itself as one of the most innovative in the cryptocurrency industry. Developed with a focus on a scientific approach and high security standards, Cardano is an advanced platform for creating decentralised applications and smart contracts. In this article, we will look at the history of Cardano’s development, the key stages of its formation and its current position in the cryptoecosystem.
Foundation and first steps
Cardano was created in 2015 by Charles Hoskinson, one of the co-founders of Ethereum. Dissatisfied with the direction of Ethereum and wanting to create a better and more secure platform, Hoskinson organised the Cardano project. The main goal was to create a blockchain platform that would solve the main problems of the then existing systems, including scalability, interoperability and resilience.
Scientific approach and development
One of the distinctive features of Cardano is its focus on a scientific approach to development. The project uses peer-reviewed research to ensure the reliability and security of the technology. The platform has been developed in co-operation with academia and research institutions such as the University of Edinburgh and the Tokyo Institute of Technology.
Launch and main stages of development
The official launch of the Cardano network took place in September 2017. The introduction of the platform’s main cryptocurrency, ADA, was an important moment for the project. Cardano uses a unique Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm called Ouroboros, which provides efficiency and reduces power consumption compared to the traditional Proof of Work used by many other blockchains.
Updates and innovations
Since its launch, Cardano has gone through several significant updates, each adding new functionality and improvements. For example, the Shelley update, launched in 2020, brought decentralisation to blockchain creation and also introduced steaking for ADA holders. The next major update, Alonzo, brought support for smart contracts, allowing developers to create complex decentralised applications on the platform.
Current situation and outlook
Today Cardano is one of the leading blockchain platforms, valued for its high level of security and reliability. Support for smart contracts and a constant strive for innovation make Cardano an attractive platform for developers and investors. The Cardano team continues to work on improving the functionality and expanding the capabilities of the platform, as well as on strengthening its position in the blockchain technology market.
Cardano’s history is an example of a successful combination of scientific approach and technological innovation in the blockchain industry. With its help, the platform has not only managed to take a significant place in the market, but also continues to contribute to the development of the entire industry, offering new solutions to create a secure and efficient digital future.
RUE customer support team
RUE (Regulated United Europe) customer support team complies with high standards and requirements of the clients. Customer support is the most complex field of coverage within any business industry and operations, that is why depending on how the customer support completes their job, depends not only on the result of the back office, but of the whole project itself. Considering the feedback received from the high number of clients of RUE from all across the world, we constantly work on and improve the provided feedback and the customer support service on a daily basis.
CONTACT US
At the moment, the main services of our company are legal and compliance solutions for FinTech projects. Our offices are located in Vilnius, Prague, and Warsaw. The legal team can assist with legal analysis, project structuring, and legal regulation.
Registration number:
14153440
Anno: 16.11.2016
Phone: +372 56 966 260
Email: [email protected]
Address: Laeva 2, Tallinn, 10111, Estonia
Registration number: 304377400
Anno: 30.08.2016
Phone: +370 6949 5456
Email: [email protected]
Address: Lvovo g. 25 – 702, 7th floor, Vilnius, 09320, Lithuania
Registration number:
08620563
Anno: 21.10.2019
Phone: +420 775 524 175
Email: [email protected]
Address: Na Perštýně 342/1, Staré Město, 110 00, Prague
Registration number: 38421992700000
Anno: 28.08.2019
Email: [email protected]
Address: Twarda 18, 15th floor, Warsaw, 00-824, Poland
Please leave your request
The RUE team understands the importance of continuous assessment and professional advice from experienced legal experts, as the success and final outcome of your project and business largely depend on informed legal strategy and timely decisions. Please complete the contact form on our website, and we guarantee that a qualified specialist will provide you with professional feedback and initial guidance within 24 hours.